1. Pan W, Huang W, Zheng J, Meng Z, Pan X. Construction of a prognosis model of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma pyroptosis and an analysis of immuno-phenotyping based on bioinformatics. Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jan 31;13(1):299-316.
2. Miao J, Tu Y, Jiang J, Ren R, Wu Q, Liang H, Wang T, Lin B, Wu J, Pan Y, Wang X, Jin H. VSIG4 inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by enhancing Nrf2-dependent antioxidant response against reactive oxygen species production. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Mar;260(Pt 2):129357.
VSIG4 (V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 4), also known as CRIg and Z39IG, is a type I transmembrane protein of the B7 family within the Ig superfamily. VSIG4 contains two Ig-like (immunoglobulin-like) domains. VSIG4 is abundantly expressed in several fetal tissues. In adult tissues, the highest expression of VSIG4 is in lung and placenta. VSIG4 functions as a negative regulator of T cell activation, and may be involved in the maintenance of peripheral T cell tolerance, and is also identified as a potent suppressor of established inflammation. VSIG4 is a phagocytic receptor, strong negative regulator of T-cell proliferation and IL2 production.
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).
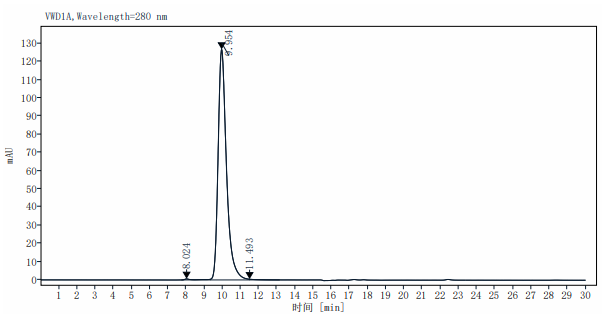
The purity of VSIG4 His Tag, Human is greater than 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC.