1. Nicklin MJ,et al. (1994) A physical map of the region encompassing the human interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist genes. Genomics. 19(2):382-4.
2. March CJ, et al. (1985) Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 315(6021):641-7.
3. Bankers-Fulbright JL, et al. (1996) Interleukin-1 signal transduction. Life Sci. 59(2):61-83.
4. Dinarello CA, et al. (1997) Induction of interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Semin Oncol. 24 (3 Suppl 9): S9-81-S9-93.
IL-1 alpha is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family. Cytokines are proteinaceous signaling compounds that are major mediators of the immune response. They control many different cellular functions including proliferation, differentiation, and cell survival/apoptosis but are also involved in several pathophysiological processes including viral infections and autoimmune diseases. Cytokines are synthesized under various stimuli by a variety of cells of both the innate (monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells) and adaptive (T- and B-cells) immune systems. Cytokines can be classified into two groups: pro- and anti-inflammatory. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IFN gamma, IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-alpha, are predominantly derived from the innate immune cells and Th1 cells. Anti-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-10, IL-4, IL-13, and IL-5, are synthesized from Th2 immune cells. IL-1 alpha is a pleiotropic cytokine involved in various immune responses, inflammatory processes, and hematopoiesis. It is produced by monocytes and macrophages as a proprotein, which is proteolytically processed and released in response to cell injury, and thus induces apoptosis. IL-1 alpha stimulates thymocyte proliferation by inducing IL-2 release, B-cell maturation and proliferation, and fibroblast growth factor activity.
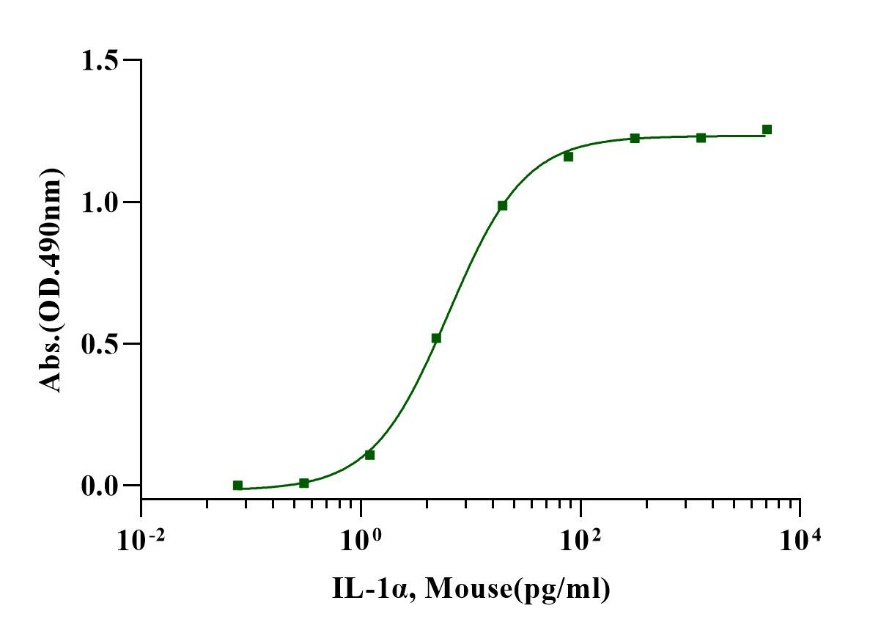
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using D10.G4.1 mouse helper T cells. The EC50 for this effect is less than 6pg/ml.

1μg (R: reducing condition,N: non-reducing condition).