P40: 35.8 kDa (Reducing)
P35: 22.5 kDa (Reducing)
Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1. Airoldi, I. et al. (2000) Journal of Immunology 165:6880.
2. Wolf, S.F. et al. (1991) Journal of Immunology 146:3074.
3. Gearing, D. et al. (1991) Cell 66:9.
4. Merberg, D. et al. (1992) Immunology Today 13:78.
5. Gubler, U. et al. (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 88:4143.
IL-12 is involved in the differentiation of naive T cells into Th1 cells. It is known as a T cell-stimulating factor, which can stimulate the growth and function of T cells. It stimulates the production of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) from T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, and reduces IL-4 mediated suppression of IFN-γ. T cells that produce IL-12 have a coreceptor, CD30, which is associated with IL-12 activity. IL-12 plays an important role in the activities of natural killer cells and T lymphocytes. IL-12 mediates enhancement of the cytotoxic activity of NK cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes.

Measured by its ability to enhance IFN-gamma secretion in NK-92 human natural killer lymphoma cells. The EC50 for this effect is less than 0.6ng/ml.

2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).
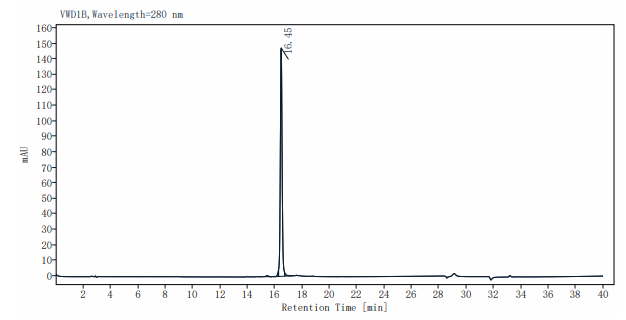
>95% as determined by RP-HPLC.