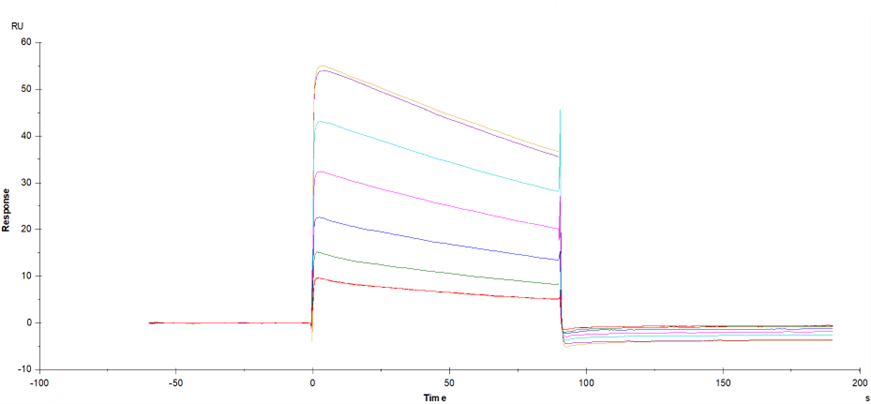
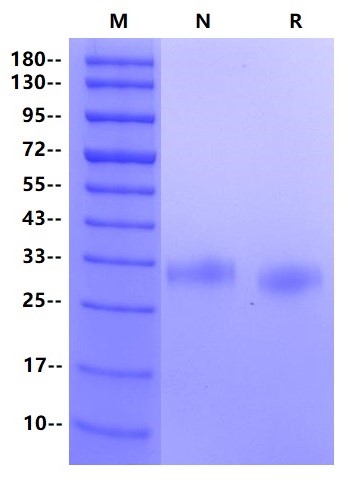
IgG Fc receptor (Fc gamma R) is a member of the Ig superfamily and plays a role in activating or suppressing immune responses. Human Fc gamma Rs can be divided into three types: RI (CD64), RII (CD32) and RIII (CD16), which can produce a variety of subtypes (1-3). Fc gamma RI is a high affinity receptor for binding monomer IgG, while Fc gamma RII and RIII are low affinity receptors for binding aggregation or immune complex IgG (IC). The extracellular domain of human Fc gamma RIIA has about 90% amino acid sequence homology with human Fc gamma RIIB and Fc gamma RIIC. Fc gamma RIIA is expressed in many immune cell types (macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, platelets, dendritic cells and Langerhans cells). Inhibition of ITIM receptors may also be co-expressed and co-participated through specific ligands. Inflammatory responses (cytolysis, phagocytosis, degranulation and production of cytokines) are initiated by Fc γ RIIA signals, which can be regulated by inhibitory receptor signals. The intensity of the signal depends on the expression ratio of the activated receptor and the inhibitory receptor. The two alleles of Fc gamma RIIA (R167 and H167) are different in the ability to connect human IgG2 or CRP.