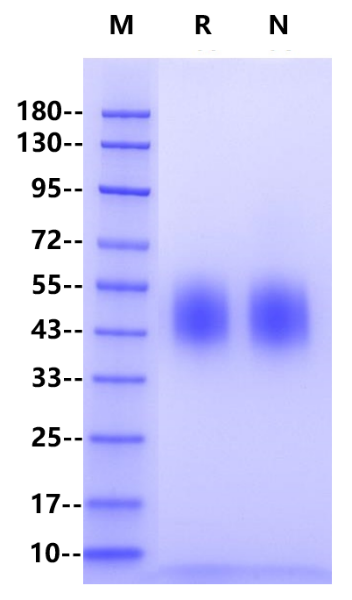
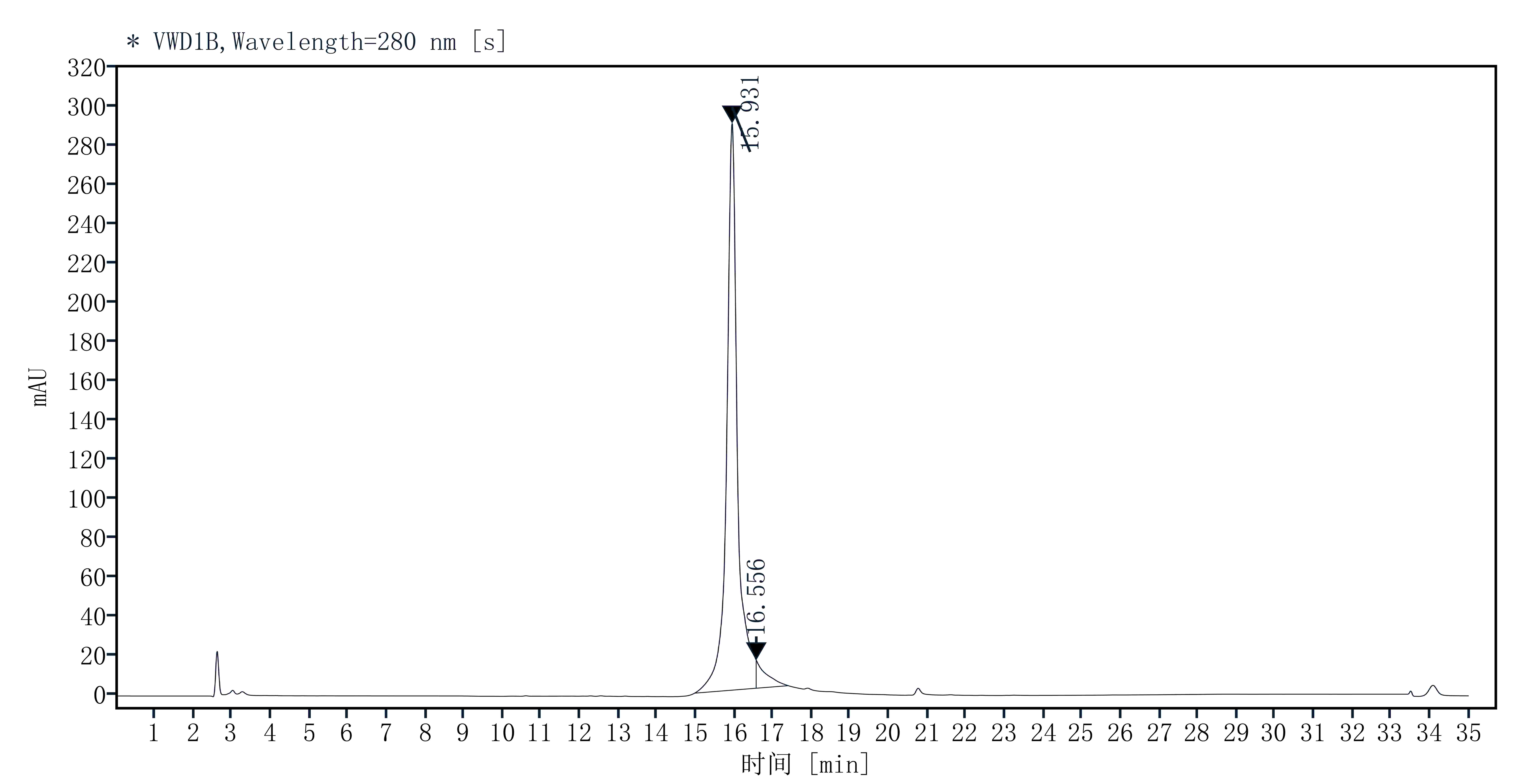
Fc epsilon RI α, also known as FCER1A, is the α subunit of immunoglobulin receptor (IgE receptor). IgE receptor consists of one α subunit, one β subunit and two γ subunits. The α subunit includes extracellular domain and transmembrane domain, and the extracellular region contains two immunoglobulin-like domains, in which the proximal membrane end is the binding region to IgE Fc, and the other end is related to high affinity. The α subunit contains seven N-chain glycosylation sites, which can guide the correct folding of the α-chain. β subunit is divided into transmembrane region and intracellular region, which is a four-time transmembrane molecule with immune receptor tyrosine activation motif (ITAM). The γ subunits are connected by disulfide bonds and each has a transmembrane region. Fc epsilon RI α first initiates anaphylaxis. Allergens act on mast cells through IgE and Fc epsilon RI α, activate chemical mast cells through signal transduction, release vasoactive mediators such as histamine and bradykinin to cause hypersensitivity, or pre-release Leucotrienes, leukotrienes and platelet activating factors to cause inflammation.
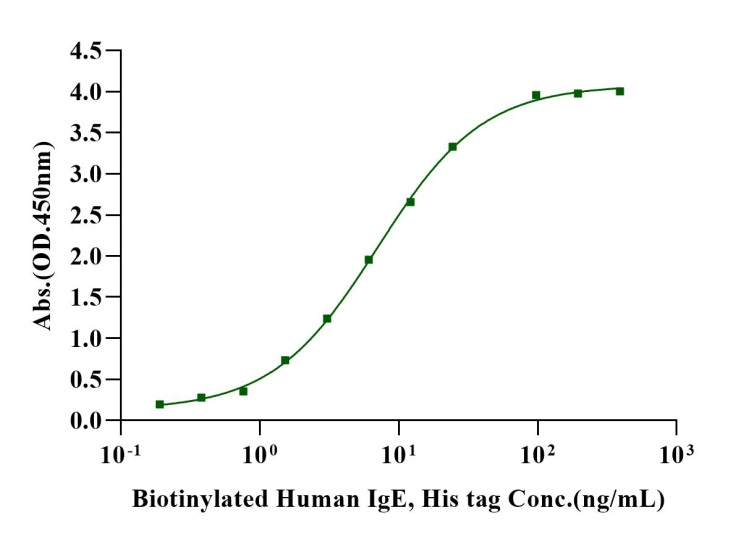
Immobilized PDGF-BB, Human (Cat. No. UA040014) at 0.5μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind CD140b/PDGFRB His Tag, Human (Cat. No. UA010514) with EC50 of 35.14-52.62 ng/mL.