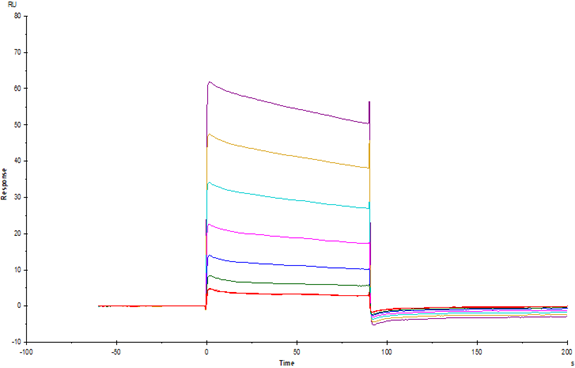
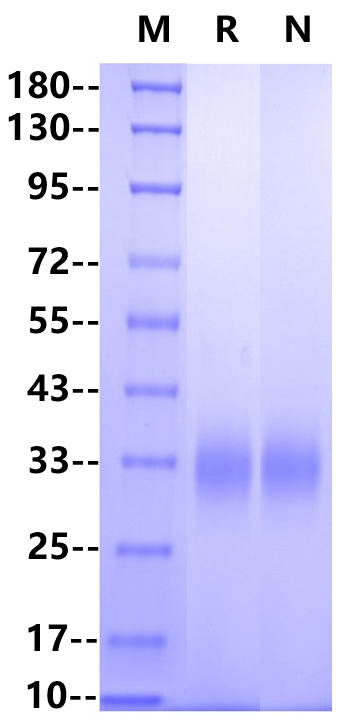
IgG Fc receptor (Fc γ R) is a member of the Ig superfamily, which plays a role in activating or inhibiting immune response. Human Fc γ Rs is identified as three types: RI (CD64), RII (CD32) and RIII (CD16) can produce multiple subtypes. There are three human Fc γ RII / CD32 genes (A, B and C), two crab eating monkeys (An and B), and one Fc γ RII B in mice. Fc γ RIIB is also called CD32b, FCG2, IGFR2. In the extracellular domain, the homology of cynomolgus monkey CD32b with human, mouse and rat is 90%, 64% and 61%, respectively. CD32 is a low affinity receptor of IgG. Fc γ RIIB was expressed on B cells, dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages and mast cells, and had the highest affinity to IgG1, followed by IgG3, IgG4 and IgG2. Fc γ RII B can regulate the survival of plasma cells, maintain the stability of the internal environment, inhibit the maturation of dendritic cells and the release of type I interferon, inhibit the antigen presentation of mature dendritic cells, and inhibit cell phagocytosis, antibody-dependent cytotoxicity and the release of inflammatory mediators.