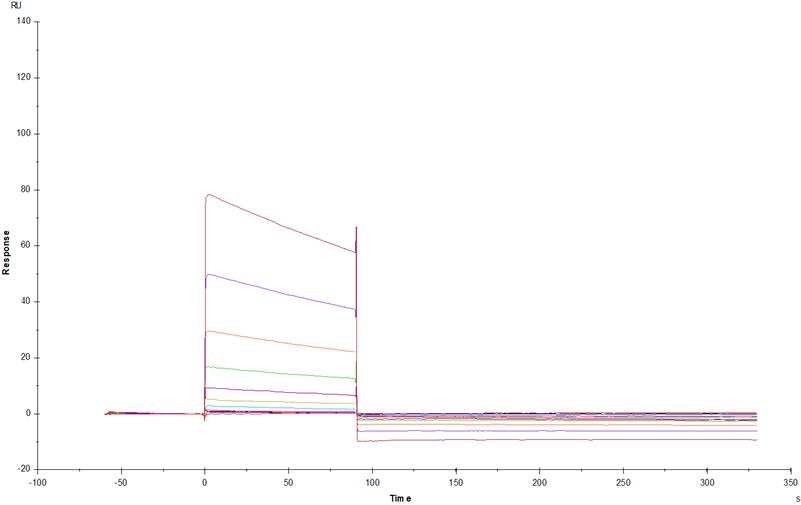
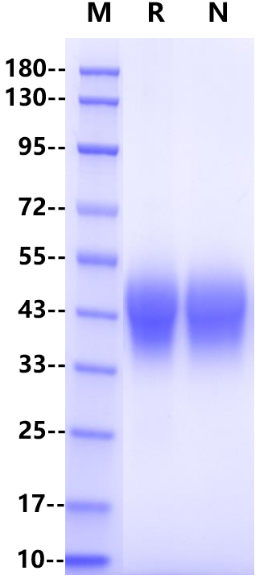
IgG Fc receptor (Fc γ R) is a member of the Ig superfamily, which plays a role in activating or inhibiting immune response. Human Fc γ Rs is identified as three types: RI (CD64), RII (CD32) and RIII (CD16) can produce multiple subtypes. CD32 is a low affinity receptor of IgG. There are 3 Fc γ RII / CD32 genes (A, B and C) in human, 2 genes in monkeys (An and B) and one Fc γ RII B in mice. Mature Fc γ RIIA is a type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein. About 40 kDa is composed of extracellular domain, transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic domain, and the extracellular domain includes two IgG domains. The extracellular domain Fc γ RIIA of rat shares 52% of the amino acid sequence with that of human Fc γ RIIA. CD32a is expressed in a variety of immune cells, such as macrophages, neutrophils, platelets and so on. Inhibition of ITIM receptors may also be co-expressed and co-participated by specific ligands to initiate inflammatory responses during ligand binding, including cytolysis, phagocytosis, degranulation and production of cytokines. This response can be regulated by co-expression of inhibitory receptors such as CD32B, and the intensity of the signal depends on the proportion of activated and inhibitory receptors.