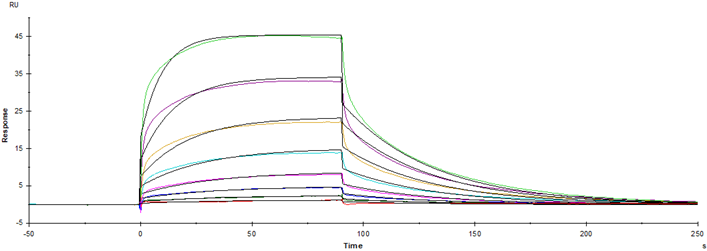
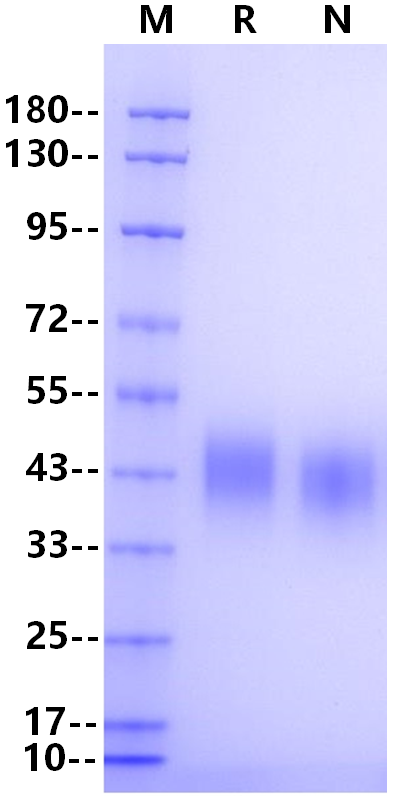
IgG Fc receptor (Fc γ R) is a member of the Ig superfamily, which plays a role in activating or inhibiting immune response. Human Fc γ Rs is identified as three types: RI (CD64), RII (CD32) and RIII (CD16). CD16 is a low-affinity Fc receptor, which has been identified as Fc receptor Fc γ RIII (a (CD16a) and Fc γ RIIIb (CD16b). These receptors bind to the Fc portion of the IgG antibody and are encoded by two different highly homologous genes in a cell type-specific manner. Mature crab-eating monkey Fc γ RIII consists of an extracellular domain of 192 amino acids, a transmembrane segment of 21 amino acids and a cytoplasmic domain of 25 amino acids. The extracellular domain has 92% and 90% amino acid homology with human Fc γ RIIIA and Fc γ RIIIB, respectively. Fc γ RIII is expressed on NK cells, T cells, monocytes and macrophages, and exists on the surface of natural killer cells, neutrophils, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes and macrophages. It is involved in phagocytosis, secretion of enzymes and inflammatory mediators, antibody-dependent cytotoxicity and clearance of immune complexes.