Asp19-Ser182, with C-terminal 8*His
DRHTVFWNSSNPKFRNEDYTIHVQLNDYVDIICPHYEDHSVADAAMEQYILYLVEHEEYQLCQPQSKDQVRWQCNRPSAKHGPEKLSEKFQRFTPFTLGKEFKEGHSYYYISKPIHQHEDRCLRLKVTVSGKITHSPQAHDNPQEKRLAADDPEVRVLHSIGHSGGGSHHHHHHHH
>95% by SDS-PAGE
EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 1 (abbreviated as Ephrin-A1) also known as ligand of eph-related kinase 1 or EFNA1, is a member of the ephrin (EPH) family. The Eph family receptor interacting proteins (ephrins) are a family of proteins that serve as the ligands of the Eph receptor, which compose the largest known subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases (RTKs). Ephrin-A1/EFNA1 and its Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases are expressed by cells of the SVZ. Ephrin subclasses are further distinguished by their mode of attachment to the plasma membrane: ephrin-A ligands bind EphA receptors and are anchored to the plasma membrane via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) linkage, whereas ephrin-B ligands bind EphB receptors and are anchored via a transmembrane domain. An exception is the EphA4 receptor, which binds both subclasses of ephrins. Ephrin-A1 and its receptor EphA2 were expressed in xenograft endothelial cells and also tumor cells and play a role in human cancers, at least in part by influencing tumor neovascularization.
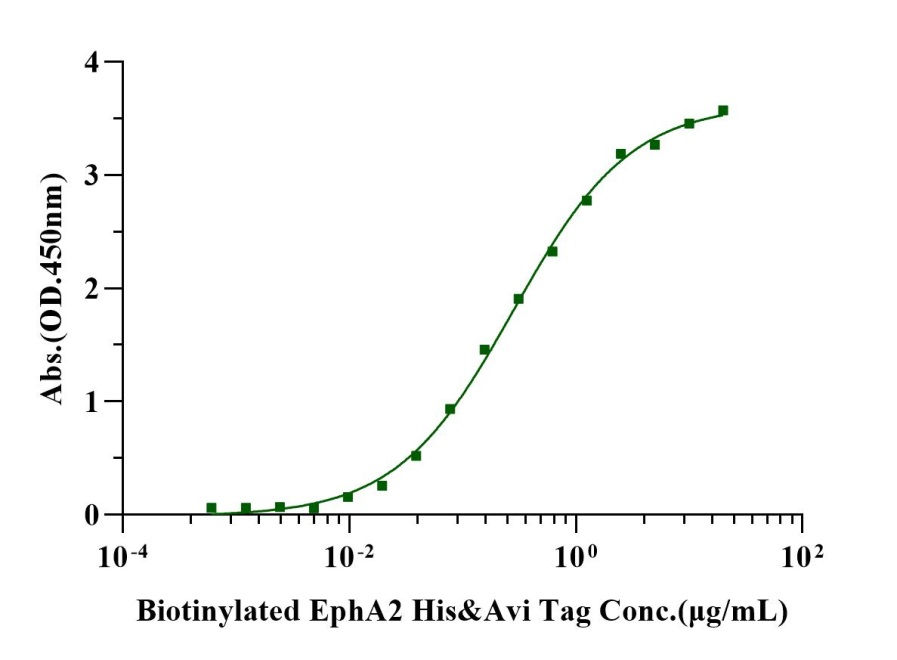
Immobilized Ephrin-A1 His Tag, Human (Cat. No. UA010170) at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind Biotinylated EphA2 His&Avi Tag (Cat. No. UA010833) with EC50 of 0.25-0.36μg/mL .