Phe22-Ala105, with C-terminal 8*His
FKIPIEELEDRVFVNCNTSITWVEGTVGTLLSDITRLDLGKRILDPRGIYRCNGTDIYKDKESTVQVHYRMCQSCVELDPATVAHHHHHHHH
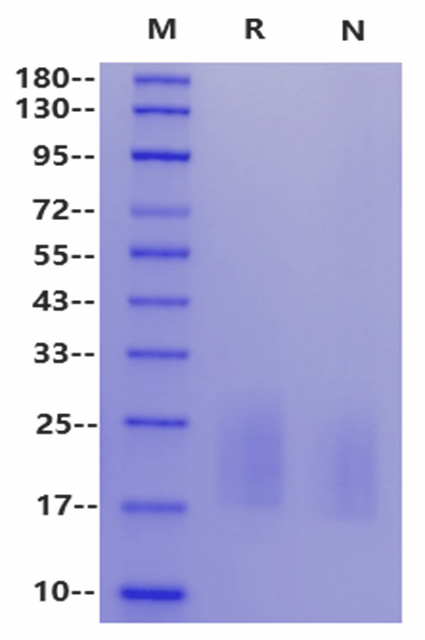
>95% by SDS-PAGE
T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 delta chain, also known as CD3D, is a single-pass type I membrane protein. CD3 delta/CD3d is part of the T-cell receptor/CD3 complex (TCR/CD3 complex) and is involved in T-cell development and signal transduction. The encoded membrane protein represents the delta subunit of the CD3 complex, and along with four other CD3 subunits, binds either TCR alpha/beta or TCR gamma/delta to form the TCR/CD3 complex on the surface of T cells. CD3 delta/CD3d contains an 84 amino acid extracellular domain, a 21 amino acid transmembrane domain, and a 45 amino acid cytoplasmic domain. Deleterious mutation of the CD3 delta encoding gene in the human leads to a severe combined immunodeficiency characterised by the complete absence of mature T cell subpopulations including TCR alpha/beta and TCR gamma/delta. In humans the absence of CD3 delta results in a complete arrest in thymocyte development at the stage of double negative to double positive transition and the development of gamma delta T-cell receptor-positive T cells is also impaired. CD3D, together with CD3 epsilon (CD3E), CD3 gamma and CD3 zeta, and the T-cell receptor alpha/beta and gamma/delta heterodimers, forms the T cell receptor-CD3 complex. T cell receptor-CD3 complex plays an important role in coupling antigen recognition to several intracellular signal-transduction pathways.