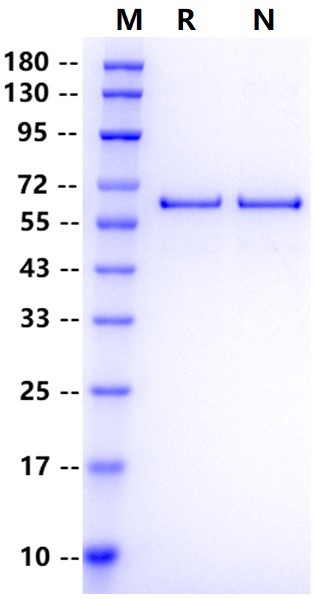
Met1-Asn498, with C-terminal 10*His MASQGTKRSYEQMETDGERQNATEIRASVGKMIGGIGRFYIQMCTELKLSDYEGRLIQNSLTIERMVLSAFDERRNKYLEEHPSAGKDPKKTGGPIYRRVNGKWMRELILYDKEEIRRIWRQANNGDDATAGLTHMMIWHSNLNDATYQRTRALVRTGMDPRMCSLMQGSTLPRRSGAAGAAVKGVGTMVMELVRMIKRGINDRNFWRGENGRKTRIAYERMCNILKGKFQTAAQKAMMDQVRESRNPGNAEFEDLTFLARSALILRGSVAHKSCLPACVYGPAVASGYDFEREGYSLVGIDPFRLLQNSQVYSLIRPNENPAHKSQLVWMACHSAAFEDLRVLSFIKGTKVLPRGKLSTRGVQIASNENMETMESSTLELRSRYWAIRTRSGGNTNQQRASAGQISIQPTFSVQRNLPFDRTTIMAAFNGNTEGRTSDMRTEIIRMMESARPEDVSFQGRGVFELSDEKAASPIVPSFDMSNEGSYFFGDNAEEYDNGGGSGGGSHHHHHHHHHH.
12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied; 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution; 1 week, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution; Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
1.Pang B, Cheung NN, Zhang W, Dai J, Kao RY, Zhang H, Hao Q. Structural Characterization of H1N1 Nucleoprotein-Nucleozin Binding Sites. Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 11;6:29684. doi: 10.1038/srep29684. PMID: 27404920; PMCID: PMC4939526.2.Ortega J, Martín-Benito J, Zürcher T, Valpuesta JM, Carrascosa JL, Ortín J. Ultrastructural and functional analyses of recombinant influenza virus ribonucleoproteins suggest dimerization of nucleoprotein during virus amplification. J Virol. 2000 Jan;74(1):156-63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.1.156-163.2000. PMID: 10590102; PMCID: PMC111524.
Nucleoprotein, encoded by influenza A virus, is an attractive target due to its high conservative and multifunctional nature during virus life cycle. In addition, NP does not have any counterpart in the cell, and hence compounds targeting NP might have less off-target side effects. NP encapsulates the negative strand viral RNA by is binding to 24 bases of RNA, protecting it from nucleases. The encapsulated genomic RNA is termed the ribonucleoprotein (RNP). The active RNP imports into the nucleus through cellular importin α/β pathways, and serves as template for transcription and replication.