Protein sequence(P17931, Met1-Ile250, with C-10*His) MADNFSLHDALSGSGNPNPQGWPGAWGNQPAGAGGYPGASYPGAYPGQAPPGAYPGQAPPGAYPGAPGAYPGAPAPGVYPGPPSGPGAYPSSGQPSATGAYPATGPYGAPAGPLIVPYNLPLPGGVVPRMLITILGTVKPNANRIALDFQRGNDVAFHFNPRFNENNRRVIVCNTKLDNNWGREERQSVFPFESGKPFKIQVLVEPDHFKVAVNDAHLLQYNHRVKKLNEISKLGISGDIDLTSASYTMIGGGGSHHHHHHHHHH
>90% by SDS-PAGE
12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied. 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution. 1 week, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution. Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pepsin is an aspartic protease, using a catalytic aspartate in its active site. Pepsin's proenzyme, pepsinogen, is released by the gastric chief cells in the stomach wall, and upon mixing with the hydrochloric acid of the gastric juice, pepsinogen activates to become pepsin. Pepsinogens are mainly grouped in 5 different groups based on their primary structure: pepsinogen A (also called pepsinogen I), pepsinogen B, progastricsin (also called pepsinogen II and pepsinogen C), prochymosin (also called prorennin) and pepsinogen F (also called pregnancy-associated glycoprotein).Pepsinogen levels in serum may serve as a biomarker for atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer.
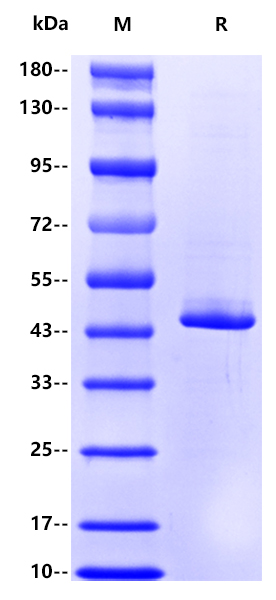
2μg(R: reducing conditions)