Protein sequence(P05112, His25-Ser153, with C-10*His) HKCDITLQEIIKTLNSLTEQKTLCTELTVTDIFAASKNTTEKETFCRAATVLRQFYSHHEKDTRCLGATAQQFHRHKQLIRFLKRLDRNLWGLAGLNSCPVKEANQSTLENFLERLKTIMREKYSKCSSGGGGSHHHHHHHHHH
Theoretical:16.6kDa Actual:20kDa
12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied. 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution. 1 week, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution. Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
The interleukin 4 (IL4, IL-4) is a cytokine that induces differentiation of naive helper T cells (Th0 cells) to Th2 cells. Upon activation by IL-4, Th2 cells subsequently produce additional IL-4 in a positive feedback loop. IL-4 is produced primarily by mast cells, Th2 cells, eosinophils and basophils. It is closely related and has functions similar to IL-13. Interleukin 4 has many biological roles, including the stimulation of activated B cell and T cell proliferation, and the differentiation of B cells into plasma cells. It is a key regulator in humoral and adaptive immunity. IL-4 induces B cell class switching to IgE, and up-regulates MHC class II production. IL-4 decreases the production of Th1 cells, macrophages, IFNγ, and dendritic cells IL-12. IL-4 has also been shown to drive mitogenesis, dedifferentiation, and metastasis in rhabdomyosarcoma. IL-4, along with other Th2 cytokines, is involved in the airway inflammation observed in the lungs of patients with allergic asthma.
Immobilized IL-4R alpha/CD124 Fc Chimera Protein, Cynomolgus (Cat. No. UA010387) at 4 μg/mL (50 μL/well) can bind Human IL-4, His tag with EC50 of 13.4-18.2 ng/mL.
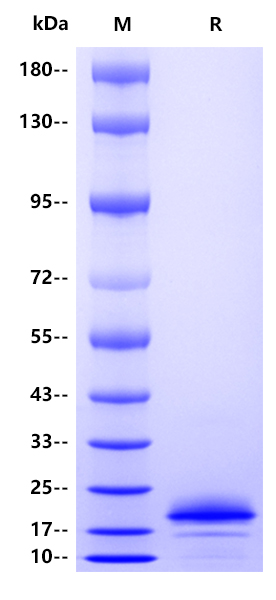
2μg (R: reducing conditions)