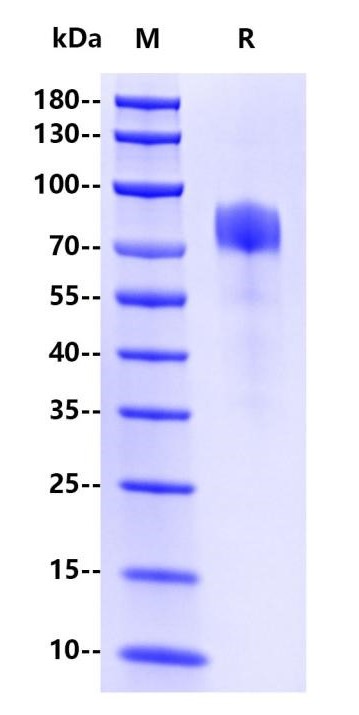
DCP (Des-gamma carboxyprothrombin) is also known as protein induced by vitamin K absence/antagonist-II (PIVKA-II). Prothrombin, a blood coagulation protein synthesized in liver, is converted to an active form after the 10 glutamic acid residues (Glu) in the γ-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) domain at positions 6, 7, 14, 16, 19, 20, 25, 26, 29 and 32 are γ-carboxylated to Gla by vitamin-K dependent γ-glutamyl carboxylase. Incomplete carboxylation of one or more Glu residues at any of the sites mentioned above may result in DCP and loss of coagulation function. Abnormal prothrombin elevation is more common in patients with vitamin K deficiency, warfarin therapy and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), so DCP can be used as a marker for HCC diagnosis. The value of this target in combination with traditional tumor marker alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the early diagnosis of HCC has been widely recognized. High PIVKA-II/DCP values indicate a potential risk of cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma and should be followed up.This product is the recombinant human PIVKA-II /DCP protein expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293).