1. Robert Sabat, Elizabeth Wallace, Stefanie Endesfelder, Kerstin Wolk. IL-19 and IL-20: two novel cytokines with importance in inflammatory diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2007 11(5):601-12.
2. Ying-Yin
Chen, Chien-Feng Li, Ching-Hua Yeh, Ming-Shi Chang, Chung-Hsi Hsing
Interleukin-19 in breast cancer. Clin Dev Immumol.2013;294320. doi:
10.1155/2013/294320
IL-19
is member of the so-called IL-10 family of cytokines. This family also
contains IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine known of for a very long time,
and six other mediators: IL-20, IL-22, IL-24, IL-26, IL-28A, IL-28B and
IL-29. The members of the IL-10 family have the following features:
clustering of their encoding genes, similar genomic structures, similar
primary and secondary protein structures and use of similar receptor
complexes. In fact, these nine proteins are encoded by genes that are found in
the human genome in three clusters and have similar exon–intron structures.
Interleukin-
(IL-) 19, part of the IL-10 family, contributes to a range of diseases and
disorders, such as asthma, endotoxic shock, uremia, psoriasis, and rheumatoid
arthritis. IL-19 is expressed in several types of tumor cells, especially in
squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, tongue, esophagus, and lung and invasive
duct carcinoma of the breast.
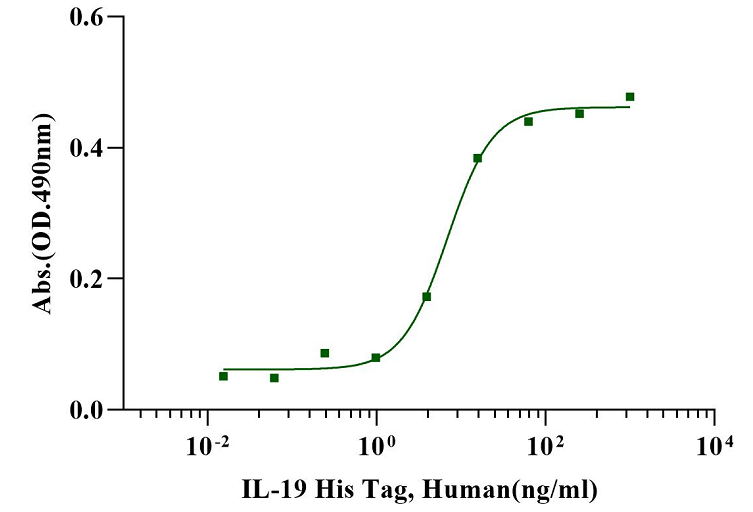
Measured in a serum-free cell proliferation assay using MCF‑7 human breast cancer cells. The EC50 for this effect is less than 20ng/mL.
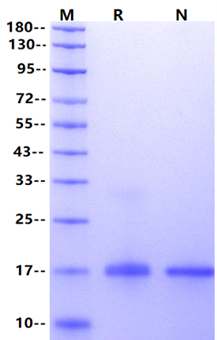
1μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).