1. Veillette, A. (2006) Immunol. Rev. 214:22. 2.Tovar, V. et al. (2002) Immunogenetics 54:394. 3.Murphy, J.J. et al. (2002) Biochem. J. 361:431.
SLAM family member 7 (SLAMF7) is also known as CD2-like receptor-activating cytotoxic cells (CRACC), Membrane protein FOAP-12, CD antigen CD319, Novel Ly9, Protein 19A, which is a single-pass type I membrane protein and a member of the CD2 family of cell surface receptors. Mature mouse CRACC consists of a 202 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD) with one Ig-like V-set domain and one Ig-like C2-set domain, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and an 88 aa cytoplasmic domain with two immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motifs ITSMs. SLAM receptors triggered by homo- or heterotypic cell-cell interactions are modulating the activation and differentiation of a wide variety of immune cells and thus are involved in the regulation and interconnection of both innate and adaptive immune response. Activities are controlled by presence or absence of small cytoplasmic adapter proteins, SH2D1A/SAP and/or SH2D1B/EAT-2. Mediates natural killer (NK) cell activation through a SH2D1A-independent extracellular signal-regulated ERK-mediated pathway. Positively regulates NK cell functions by a mechanism dependent on the adapter SH2D1B. In addition to heterotypic NK cells-target cells interactions also homotypic interactions between NK cells may contribute to activation. However, in the absence of SH2D1B, inhibits NK cell function.
1μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).
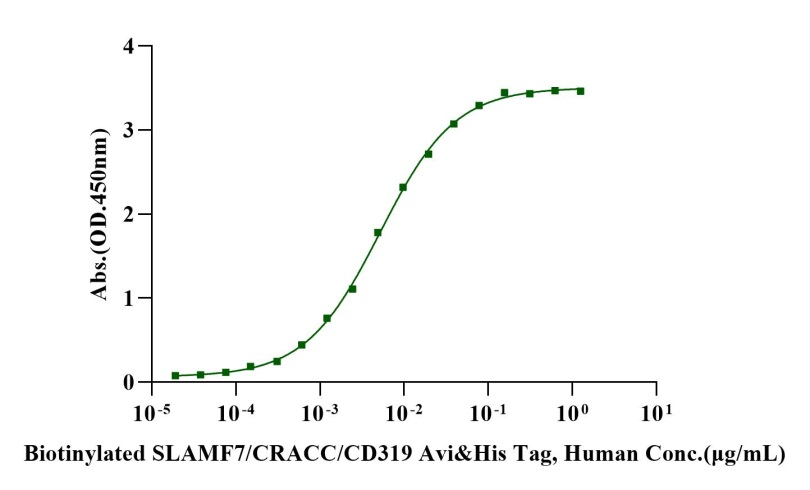
Immobilized Anti-Human SLAMF7 Monoclonal Antibody at 2μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind Biotinylated SLAMF7/CRACC/CD319 Avi&His Tag, Human (Cat. No. UA010726) with EC50 of 4.87-5.56ng/ml.