50-55kDa (Reducing)
1. Gavin R Owen, (2016) Human CD4 Metastability Is a Function of the Allosteric Disulfide Bond in Domain 2. Biochemistry. 55(15):2227-37.
The cluster of differentiation 4 receptor (CD4) is a 55kDa type I integral membrane glycoprotein which plays a substantial role during adaptive immune responses. In T-cells, CD4 mediates maturation, stabilizes T-cell receptor interactions with peptide-major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII) complexes on antigen presenting cells, and mediates intracellular T-cell signalling.2 In addition to T-cells, CD4 has also been shown to be expressed on monocytes, monocyte-derived macrophages, Langerhans cells, B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, eosinophils, megakaryocytes and mast cells. The role of CD4 during immune function can also be diverted by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope glycoprotein gp120 as the viral receptor utilizes CD4 as the primary receptor as well as the co-receptor CCR5/CXCR4 during the entry process.
1μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).
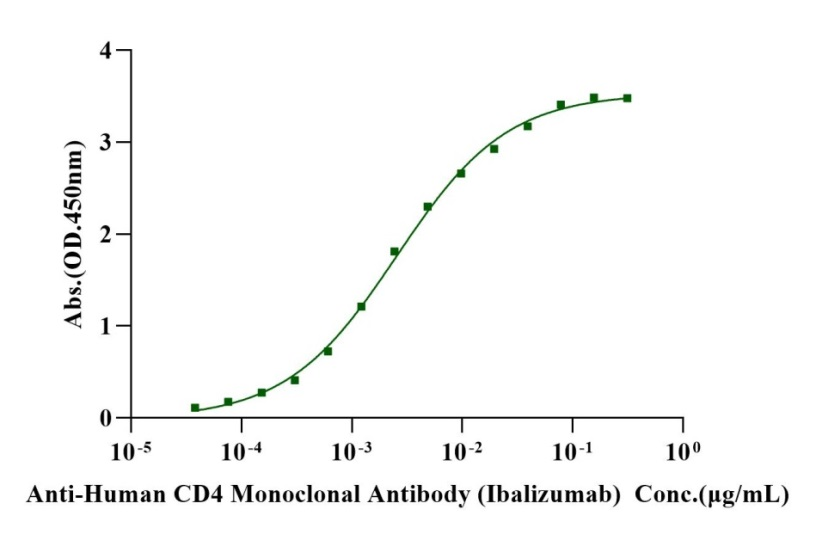
Immobilized Biotinylated CD4/LEU3 His&Avi Tag, Cynomolgus (Cat. No. UA010832) at 2 μg/mL on Streptavidin precoated (0.5μg/well) plate, can bind Anti-Human CD4 Monoclonal Antibody(Ibalizumab) with EC50 of 2.21-2.95ng/ml.