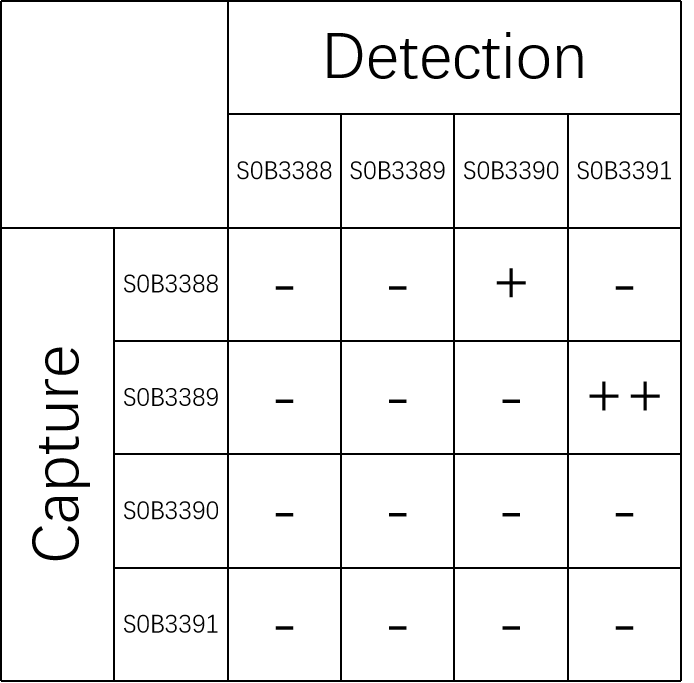
No cross reactivity against Apolipoprotein A-I, Apolipoprotein E
PBS pH7.4, 0.03% Proclin 300
12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied
Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2), also known as plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase, is an enzyme encoded by the PLA2G7 gene and belongs to the phospholipase A2 superfamily. It is primarily associated with lipoproteins in the bloodstream and plays a crucial role in lipid metabolism and inflammation. Lp-PLA2 hydrolyzes oxidized phospholipids, such as oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL), into lysophosphatidylcholine and non-esterified fatty acids, contributing to the progression of atherosclerosis. Additionally, Lp-PLA2 (Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2) serves as a biomarker for vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. It is specifically expressed in atherosclerotic plaques and associated with plaque instability. Elevated Lp-PLA2 levels independently predict increased risk of cardiovascular events (e.g., heart attack, stroke), particularly in individuals without traditional risk factors. While not diagnostic for specific diseases, it aids in risk stratification and may guide targeted preventive therapies.