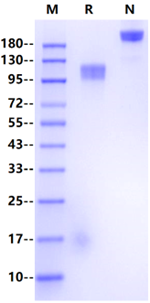
100-120kDa
Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1、Sapi E. et al. (2004) The role of CSF-1 in normal physiology of mammary gland and breast cancer: an update. Exp Biol Med. 229(1): 1-11.
1、Jang M H. et al. (2006) Distinct in vivo roles of colony-stimulating factor-1 isoforms in renal inflammation. J Immunol. 177(6): 4055-4063.
1、Cao Q. et al. (2014) Failed renoprotection by alternatively activated bone marrow macrophages is due to a proliferation-dependent phenotype switch in vivo. Kidney Int. 85(4): 794-806.
Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) is also known as macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor (M-CSFR), CD115 Cluster of Differentiation 115 (CD115), C-FMS, CSFR, FIM2, FMS, and is a member of the type Ⅲ subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases. M-CSF receptor, the product of the c-fms proto-oncogene, is a member of the type III subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases that also includes receptors for SCF and PDGF. These receptors each contain five immunoglobulin-like domains in their extracellular domain (ECD) and a split kinase domain in their intracellular region. M-CSF receptor is expressed primarily on cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage, dendritic cells, stem cells and in the developing placenta. M-CSF R engagement is continuously required for macrophage survival and regulates lineage decisions and maturation of monocytes, macrophages, osteoclasts and DC. M-CSF R and integrin alpha v beta 3 share signaling pathways during osteoclastogenesis and deletion of either causes osteopetrosis. In the brain, microglia expressing increased M-CSF R are concentrated with Alzheimers a beta peptide, but their role in pathogenesis is unclear.
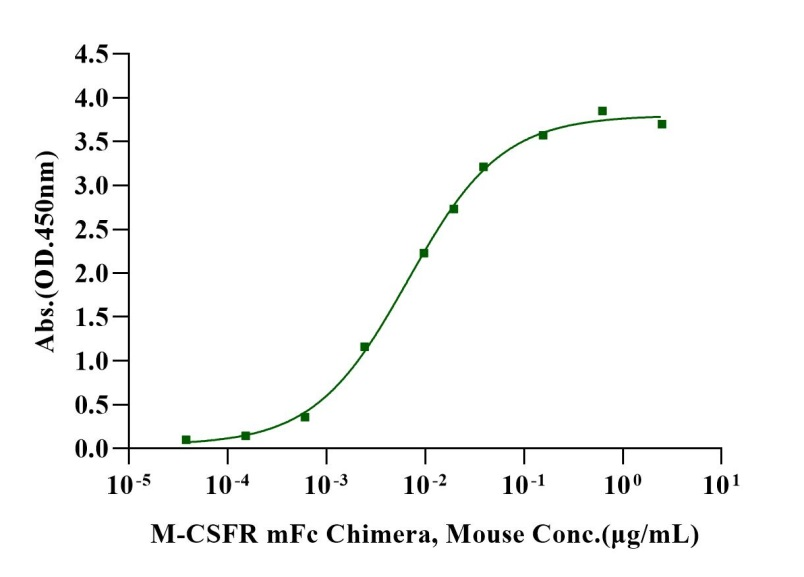
Immobilized M-CSF Protein, Mouse (Cat. No. UA040128) at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind M-CSFR mFc Chimera, Mouse(Cat. No. UA010188) with EC50 of 5.52-8.06 ng/ mL.