Typ23-Val550, with C-terminal 10*His WPGDCSHVSNNQVVLLDTTTVLGELGWKTYPLNGWDAITEMDEHNRPIHTYQVCNVMEPNQNNWLRTNWISRDAAQKIYVEMKFTLRDCNSIPWVLGTCKETFNLFYMESDESHGIKFKPNQYTKIDTIAADESFTQMDLGDRILKLNTEIREVGPIERKGFYLAFQDIGACIALVSVRVFYKKCPFTVRNLAMFPDTIPRVDSSSLVEVRGSCVKSAEERDTPKLYCGADGDWLVPLGRCICSTGYEEIEGSCHACRPGFYKAFAGNTKCSKCPPHSLTYMEATSVCQCEKGYFRAEKDPPSMACTRPPSAPRNVVFNINETALILEWSPPSDTGGRKDLTYSVICKKCGLDTSQCEDCGGGLRFIPRHTGLINNSVIVLDFVSHVNYTFEIEAMNGVSELSFSPKPFTAITVTTDQDAPSLIGVVRKDWASQNSIALSWQAPAFSNGAILDYEIKYYEKEHEQLTYSSTRSKAPSVIITGLKPATKYVFHIRVRTATGYSGYSQKFEFETGDETSDMAAEQGQILVGGGSGGGSHHHHHHHHHH
1. Gitanjali Das, Qili Yu, Ryan Hui, Kenneth Reuhl, Nicholas W. Gale & Renping Zhou Cell & Bioscience volume 6, Article number: 48 (2016).
Ephrin-a receptor 6, also known as EphA6 or EHK2, belongs to the Ephrin receptor subfamily of the protein tyrosine kinase family. The Eph family is the largest group of related receptor tyrosine kinases known, consisting of 16 members in the vertebrate genome. Eph receptor and its ligand ephrin play an important role in neuronal migration, axon binding and specific target guidance, dendritic spine formation and neuroplasticity. Studies have shown that EphA5 and EphA6 are significantly expressed in perinatal development and in the cerebral cortex of adult mice, so EphA5 and EphA6 play an important role in regulating the cellular structure of cortical neurons.

2μg (R: reducing conditions, N: non-reducing conditions).

Immobilized EphA6 His Tag, Human (Cat. No. UA010591) at 1.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind Ephrin-A3 Fc Chimera, Human (Cat. No. UA010141) with EC50 of 0.71-1.11μg/ml.
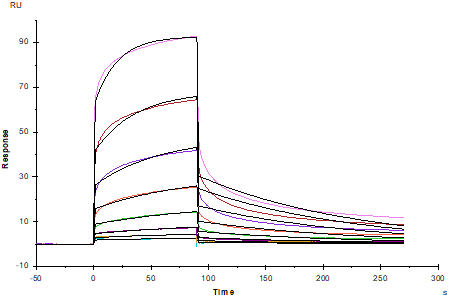
Protein A Chip captured Ephrin-A3 Fc Chimera, Human (Cat. No. UA010141), can bind EphA6 His Tag, Human (Cat. No. UA010591) with an affinity constant of 0.35μM as determined in SPR assay.