Thr38 -Val478, with C-terminal 10*His TQNKALPENVKYGIVLDAGSSHTSLYIYKWPAEKENDTGVVHQVEECRVKGPGISKFVQKVNEIGIYLTDCMERAREVIPRSQHQETPVYLGATAGMRLLRMESEELADRVLDVVERSLSNYPFDFQGARIITGQEEGAYGWITINYLLGKFSQKTRWFSIVPYETNNQETFGALDLGGASTQVTFVPQNQTIESPDNALQFRLYGKDYNVYTHSFLCYGKDQALWQKLAKDIQVASNEILRDPCFHPGYKKVVNVSDLYKTPCTKRFEMTLPFQQFEIQGIGNYQQCHQSILELFNTSYCPYSQCAFNGIFLPPLQGDFGAFSAFYFVMKFLNLTSEKVSQEKVTEMMKKFCAQPWEEIKTSYAGVKEKYLSEYCFSGTYILSLLLQGYHFTADSWEHIHFIGKIQGSDAGWTLGYMLNLTNMIPAEQPLSTPLSHSTYVGGGSGGGSHHHHHHHHHH
70-80kDa
Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1. Grinthal, A. and G. Guidotti. (2004) Biochemistry 43:13849. 2.Robson, S.C. et al. (2006) Purinergic Signal. 2:409. 3.Zebisch, M. et al. (2012) J. Mol. Biol. 415:288.
CD39, also known as ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1 (NTPDase-1), is the prototypical member of the NTPDase family. CD39 is a metal-dependent, homodimeric enzyme bound to the cell membrane through two transmembrane domains present at each termini. CD39 hydrolyzes the beta - and gamma phosphate residues of nucleotides to terminate purinergic signaling and is uniquely capable of processive hydrolysis of extracellular ATP to AMP without release of the ADP intermediate as the initial rate-limiting steps in the production of extracellular adenosine. CD39 ecto-nucleotidase is the rate-limiting enzyme of a cascade leading to the generation of suppressive adenosine that alters CD4 and CD8 T cell and natural killer cell antitumor activities.
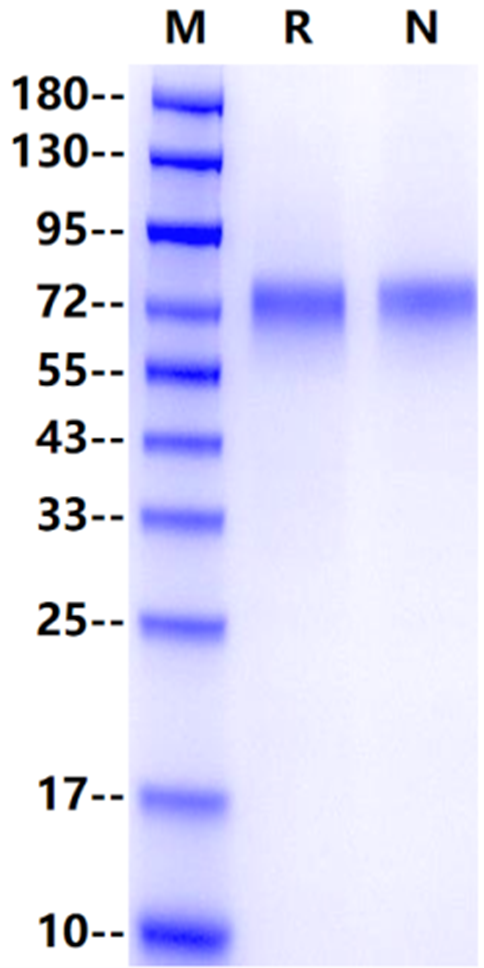
1μg (R: reducing conditions, N: non-reducing conditions).
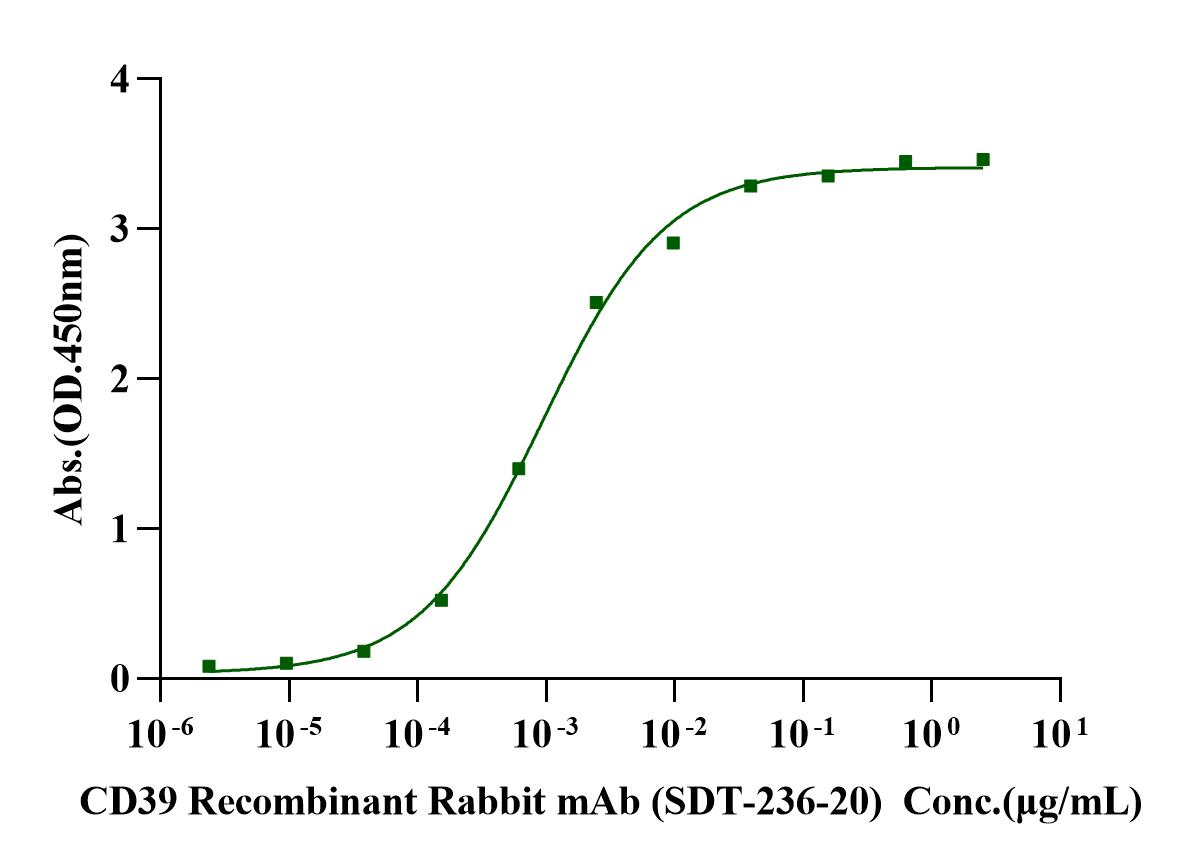
Immobilized CD39/ENTPD1 His Tag Protein, Human (Cat. No. UA010585) at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind CD39 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-236-20) (Cat. No. S0B0050) with EC50 of 0.76-1.17ng/mL.