Ala23-Ala344, with C-terminal 8*His AQNITARIGEPLVLKCKGAPKKPPQRLEWKLNTGRTEAWKVLSPQGGGPWDSVARVLPNGSLFLPAVGIQDEGIFRCQAMNRNGKETKSNYRVRVYQIPGKPEIVDSASELTAGVPNKVGTCVSEGSYPAGTLSWHLDGKPLVPNEKGVSVKEQTRRHPETGLFTLQSELMVTPARGGDPRPTFSCSFSPGLPRHRALRTAPIQPRVWEPVPLEEVQLVVEPEGGAVAPGGTVTLTCEVPAQPSPQIHWMKDGVPLPLPPSPVLILPEIGPQDQGTYSCVATHSSHGPQESRAVSISIIEPGEEGPTAGSVGGSGLGTLALAGGGSHHHHHHHH
1.Vissing H., Aagaard L., Tommerup N., Boel E. Localization of the human gene for advanced glycosylation end product-specific receptor (AGER) to chromosome 6p21.3. Genomics. 1994;24(3):606–608.
2.Yan S. D., Chen X., Fu J., et al. RAGE and amyloid-β peptide neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 1996;382(6593):685–691.
3.Deane R., du Yan S., Submamaryan R. K., et al. RAGE mediates amyloid-β peptide transport across the blood-brain barrier and accumulation in brain. Nature Medicine. 2003;9(7):907–913.
4.Krechler T., Jáchymová M., Mestek O., Žák A., Zima T., Kalousová M. Soluble receptor for advanced glycation end-products (sRAGE) and polymorphisms of RAGE and glyoxalase I genes in patients with pancreas cancer. Clinical Biochemistry. 2010;43(10-11):882–886. 2010.04.004.
AGER (advanced glycation end-product-specific receptor encodes a cell surface receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE). This gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 6: 6p21.3. This locus is involved in inflammatory and immune responses and is also the locus of major histocompatibility complex III. Recently, sRAGE was demonstrated as a new biomarker for lung cancer and RAGE could be a potential therapeutic target in Alzheimer's disease. The genetic background of RAGE demonstrated that some gene polymorphisms are implicated in various pathological states, for example, diabetes complications, amplification of the inflammatory response, non-small cell lung cancer, gastric cancer, or breast cancer.
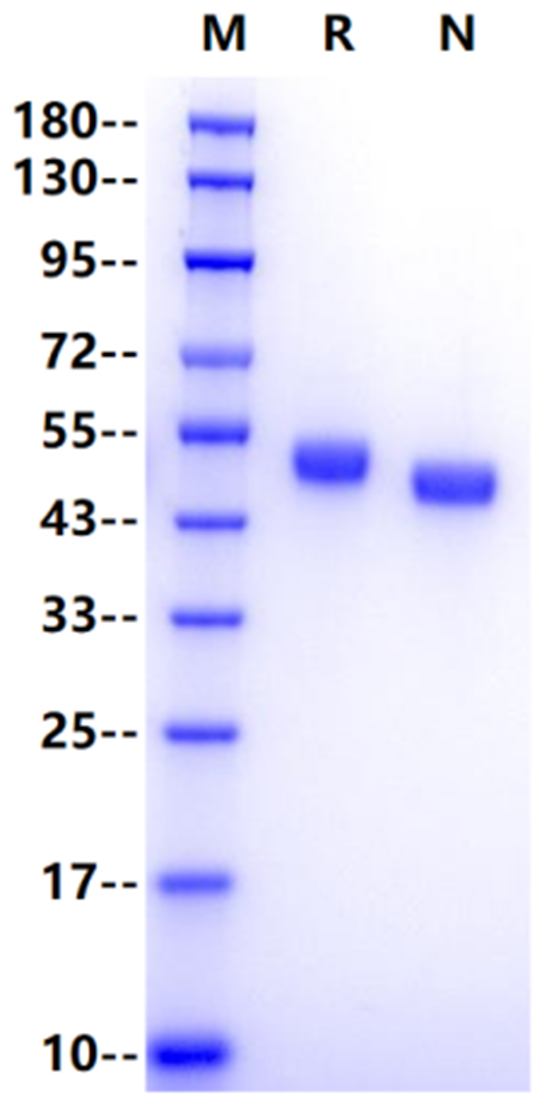
1μg (R: reducing conditions, N: non-reducing conditions).