Met1-Leu164, with C terminal 8*His Tag MVNPTVFFDITADDEPLGRVSFELFADKVPKTAENFRALSTGEKGFGYKGSSFHRIIPGFMCQGGDFTRHNGTGGRSIYGEKFEDENFILKHTGPGILSMANAGPNTNGSQFFICTAKTEWLDGKHVVFGKVKEGMNIVEAMERFGSRNGKTSKKITISDCGQLHHHHHHHH
1. Haendler B., et al.,(1987), Complementary DNA for human T-cell cyclophilin. EMBO J. 6:947-950. 2. Haendler B., et al., (1990), Characterization of the human cyclophilin gene and of related processed pseudogenes.Eur. J. Biochem. 190:477-482. 3. Ota T., et al.,(2004), Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs.Nat. Genet. 36:40-45.
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A, also known as PPIase A, Rotamase A, Cyclophilin A, Cyclosporin A-binding protein, PPIA and CYPA, is a cytoplasm protein that belongs to the cyclophilin-type PPIase family and PPIase A subfamily. Cyclophilins (CyPs) are a family of proteins found in organisms ranging from prokaryotes to humans. These molecules exhibit peptidyl-prolyl isomerase activity, suggesting that they influence the conformation of proteins in cells. PPIA / Cyclophilin A accelerate the folding of proteins. It catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides. PPIA / Cyclophilin A is secreted by vascular smooth muscle cells in response to inflammatory stimuli, and could thus contribute to atherosclerosis. It is not essential for mammalian cell viability. PPIA / Cyclophilin A can interact with several HIV proteins, including p55 gag, Vpr, and capsid protein, and has been shown to be necessary for the formation of infectious HIV virions.
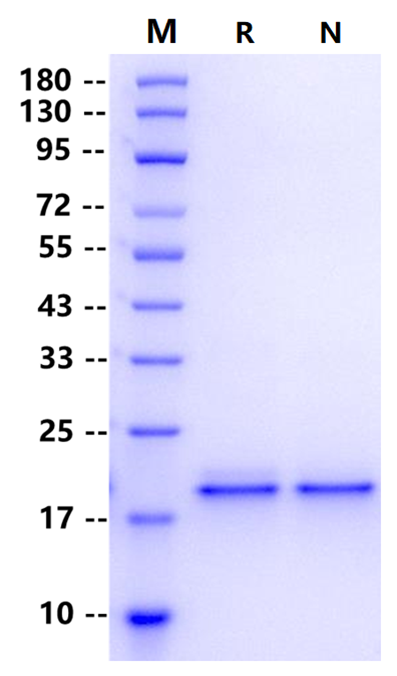
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).