1. Dhawan P, et al. Role of CXCL1 in tumorigenesis of melanoma. J Leukoc Biol. 2002 Jul;72(1):9-18.
2. Haskill S, et al. Identification of three related human GRO genes encoding cytokine functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7732-6.
3. Moser B, et al. Neutrophil-activating properties of the melanoma growth-stimulatory activity. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1797-802.
4. Vries MH, et al. CXCL1 promotes arteriogenesis through enhanced monocyte recruitment into the peri-collateral space. Angiogenesis. 2015 Apr;18(2):163-71.
CXCL1, also known as GRO-α, is a polypeptide that is initially isolated from human melanoma cells. CXCL1 acts as a key chemoattractant for neutrophils by binding specifically to its corresponding G-protein-coupled receptor CXCR2. CXCL1 modulates angiogenesis, tumorigenesis, and wound healing. In general, CXCL1 levels are extremely low under normal physiological conditions and greatly increased during inflammatory conditions. CXCL1 can also induce recruitment of regulatory T cells (Treg) and MSCs into the tumor niche. Another no-less-important property of CXCL1 is its ability to induce angiogenesis.
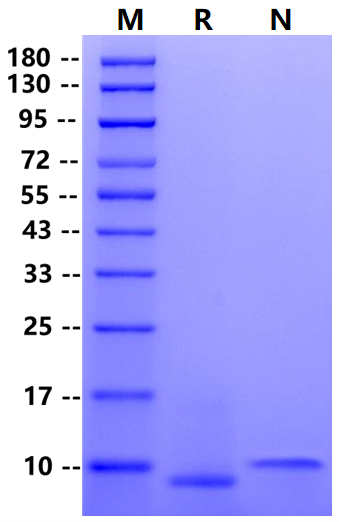
2μg (R: reducing
condition, N: non-reducing condition).