Met20-Ser220, with C-terminal Human IgG Fc MVPPPENVRMNSVNFKNILQWESPAFAKGNLTFTAQYLSYRIFQDKCMNTTLTECDFSSLSKYGDHTLRVRAEFADEHSDWVNITFCPVDDTIIGPPGMQVEVLADSLHMRFLAPKIENEYETWTMKNVYNSWTYNVQYWKNGTDEKFQITPQYDFEVLRNLEPWTTYCVQVRGFLPDRNKAGEWSEPVCEQTTHDETVPSIEGRMDPKSSDKTHTCPPCPAPELLGGPSVFLFPPKPKDTLMISRTPEVTCVVVDVSHEDPEVKFNWYVDGVEVHNAKTKPREEQYNSTYRVVSVLTVLHQDWLNGKEYKCKVSNKALPAPIEKTISKAKGQPREPQVYTLPPSRDELTKNQVSLTCLVKGFYPSDIAVEWESNGQPENNYKTTPPVLDSDGSFFLYSKLTVDKSRWQQGNVFSCSVMHEALHNHYTQKSLSLSPGK
1. Lutfalla, G. et al. (1993) Genomics 16:366. 2. Xie, M.-H. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:31335. 3. Kotenko, S.V. et al. (2003) Nat. Immunol. 4:69. 4. Yoon, S.I. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:35088.
Interleukin 10 receptor, beta subunit (IL10RB/IL-10RB) also known as Cytokine receptor family 2 member 4, Interleukin-10 receptor subunit 2, and cytokine receptor family II, member 4, is a subunit for the interleukin-10 receptor. Some members of the IL-10 family are monomeric cytokines and interact with single molecules of IL-10 R beta and their ligand‑specific subunit. Mature human IL-10 R beta consists of a 201 amino acid (aa) extracellular region with two fibronectin type-III domains, a 22 aa transmembrane segment and a 83 aa cytoplasmic domain. IL‑10 R beta is widely expressed, while the associated receptor subunits exhibit differential expression patterns. The ligand‑specific subunits are responsible for the divergent functions of these cytokines, encompassing immune suppression, promotion or inhibition of inflammation, mucosal defense, antiviral immunity, and hematopoiesis. IL-10 R beta deficient mice lack responsiveness to each of those cytokines. IL-10 R beta contributes to ligand binding, but effective signaling is only triggered in the presence of the ligand‑specific subunit. In the case of IL-10, a cytokine dimer binds to two IL‑10 R alpha /IL-10R1 chains, resulting in recruitment of two IL-10 R beta /IL-10R2 chains.
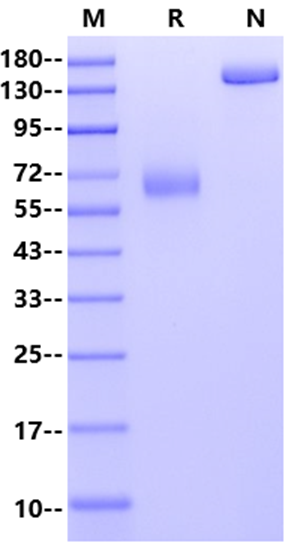
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).