Gly30-Asn439, with C-terminal 10*His GDMLIQKTIKKEVVLEEGTIAFKNWVKTGTEIYRQFWIFDVQNPQEVMMNSSNIQVKQRGPYTYRVRFLAKENITQDPKDNTVSFLQPNGAIFEPSLSVGTEADNFTVLNLAVAAASHIYPNPFVQVVLNSLINKSKSSMFQVRTLRELLWGYTDPFLSLVPYPVSTRVGMFYPYNNTADGVYKVFNGKDSISKVAIIDTYKGKRNLSYWESYCDMINGTDAASFPPFVEKSQVLQFFSSDICRSIYAVFESDVNLKGIPVYRFVLPSKAFASPVQNPDNHCFCTEKIISKNCTSYGVLDISKCKEGKPVYISLPHFLYASPDVSETIDGLNPNEEEHRTYLDIEPITGFTLQFAKRLQVNLLVKPSNKIQVLKRLKRNYIVPILWLNETGTIGDEKAKMFRSQVTGKINGGGSGGGSHHHHHHHHHH
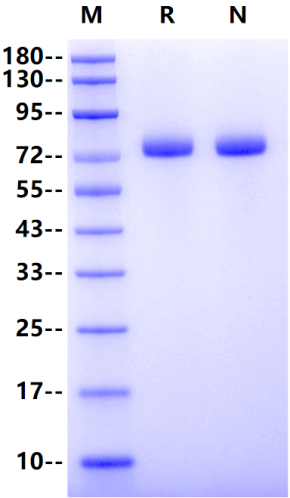
72-82kDa
Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1、Okamoto F. et al. (1998) CD36 abnormality and impaired myocardial long-chain fatty acid uptake in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Jpn Circ J. 62: 499-504.
2、Tanaka T. et al. (1997) Is CD36 deficiency an etiology of hereditary hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? J Mol Cell Cardiol. 29: 121-127.
3、Forte E. et al. (2018) The interstitium in cardiac repair: role of the immune-stromal cell interplay. Nat Rev Cardiol. 15: 601-616.
4、Coraci I S. et al. (2002) CD36, a class B scavenger receptor, is expressed on microglia in Alzheimer’s disease brains and can mediate production of reactive oxygen species in response to -amyloid fibrils. Am. J. Pathol. 160: 101-112.
CD36 belongs to the scavenger receptor class B (SR-B), a family of highly glycosylated transmembrane receptors with a wide range of ligand recognition sites. It has been reported that glycosylation of CD36 is required for trafficking of intracellular CD36 to the cell surface membrane. Because of its wide range of ligands, CD36 has plenty of functions, including but not limited to recognizing and ingesting lipids, participating in the process of inflammatory response, signal transduction, and apoptosis. The expression occurs in monocytes/macrophages and microglia as well as various other cells and tissues, including microvascular endothelial cells, platelets, adipocytes, and the heart. CD36 promotes the podocyte injury in many kidney diseases including primary nephrotic syndrome, obesity-related glomerulopathy, and diabetic nephropathy. Moreover, genetic knockout or antagonist blockade of CD36 could alleviate kidney injury indicating that CD36 is a potential therapeutic target.

Immobilized CD36/SR-B3 His Tag Protein, Cynomolgus (Cat. No. UA010265) at 2μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind CD36 Recombinant Rabbit mAb,PBS Only (SDT-358-19) (Cat. No. S0B2216) with EC50 of 2.35-2.90ng/ml.