Cys32-His430, with C-terminal human IgG Fc CPTSCKCSASRIWCSDPSPGIVAFPRLEPNSVDPENITEIFIANQKRLEIINEDDVEAYVGLRNLTIVDSGLKFVAHKAFLKNSNLQHINFTRNKLTSLSRKHFRHLDLSELILVGNPFTCSCDIMWIKTLQEAKSSPDTQDLYCLNESSKNIPLANLQIPNCGLPSANLAAPNLTVEEGKSITLSCSVAGDPVPNMYWDVGNLVSKHMNETSHTQGSLRITNISSDDSGKQISCVAENLVGEDQDSVNLTVHFAPTITFLESPTSDHHWCIPFTVKGNPKPALQWFYNGAILNESKYICTKIHVTNHTEYHGCLQLDNPTHMNNGDYTLIAKNEYGKDEKQISAHFMGWPGIDDGANPNYPDVIYEDYGTAANDIGDTTNRSNEIPSTDVTDKTGREHIEGRMDPKSSDKTHTCPPCPAPELLGGPSVFLFPPKPKDTLMISRTPEVTCVVVDVSHEDPEVKFNWYVDGVEVHNAKTKPREEQYNSTYRVVSVLTVLHQDWLNGKEYKCKVSNKALPAPIEKTISKAKGQPREPQVYTLPPSRDELTKNQVSLTCLVKGFYPSDIAVEWESNGQPENNYKTTPPVLDSDGSFFLYSKLTVDKSRWQQGNVFSCSVMHEALHNHYTQKSLSLSPGK
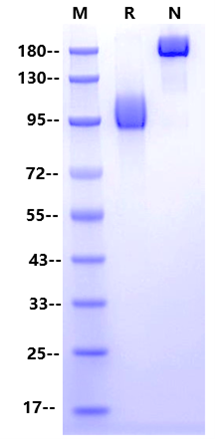
>95% by SDS-PAGE
TrkB gene encodes a member of the neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) family. This kinase is a membrane-bound receptor that, upon neurotrophin binding, phosphorylates itself and members of the MAPK pathway. Signalling through this kinase leads to cell differentiation. Mutations in this gene have been associated with obesity and mood disorders. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 2 (NTRK2) is also known as BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor, Tropomyosin-related kinase B (TRKB) and TrkB tyrosine kinase, which belongs to the protein kinase superfamily or Tyr protein kinase family. Insulin receptor subfamily. NTRK2/TrkB contains two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains, two LRR (leucine-rich) repeats, one LRRCT domain, one LRRNT domain, one protein kinase domain. NTRK2/TrkB involved in the development and the maturation of the central and the peripheral nervous systems through regulation of neuron survival, proliferation, migration, differentiation, and synapse formation and plasticity.

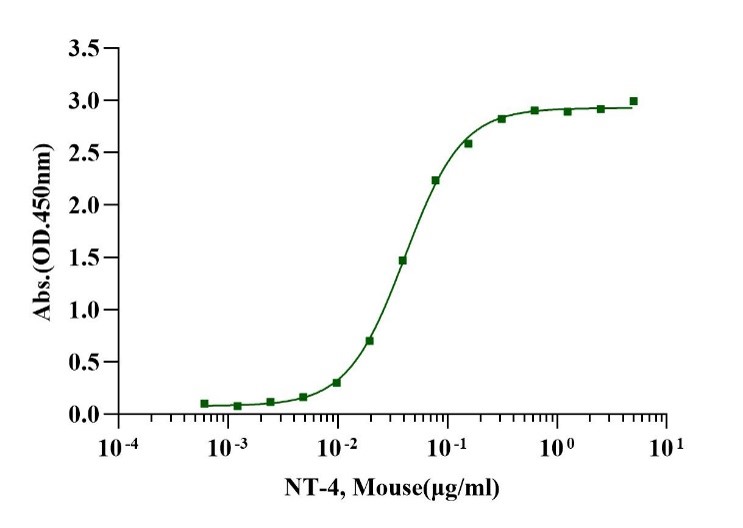
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. When Recombinant Mouse NT-4 is immobilized 2µg/mL (100 µl/well), Recombinant Human TrκB Fc chimera binds with an EC50 of 0.3-0.4μg/ml.