Leu36-Tyr482
LNFRAPPVIPNVPFLWAWNAPSEFCLGKFDEPLDMSLFSFIGSPRINATGQGVTIFYVDRLGYYPYIDSITGVTVNGGIPQKISLQDHLDKAKKDITFYMPVDNLGMAVIDWEEWRPTWARNWKPKDVYKNRSIELVQQQNVQLSLTEATEKAKQEFEKAGKDFLVETIKLGKLLRPNHLWGYYLFPDCYNHHYKKPGYNGSCFNVEIKRNDDLSWLWNESTALYPSIYLNTQQSPVAATLYVRNRVREAIRVSKIPDAKSPLPVFAYTRIVFTDQVLKFLSQDELVYTFGETVALGASGIVIWGTLSIMRSMKSCLLLDNYMETILNPYIINVTLAAKMCSQVLCQEQGVCIRKNWNSSDYLHLNPDNFAIQLEKGGKFTVRGKPTLEDLEQFSEKFYCSCYSTLSCKEKADVKDTDAVDVCIADGVCIDAFLKPPMETEEPQIFY
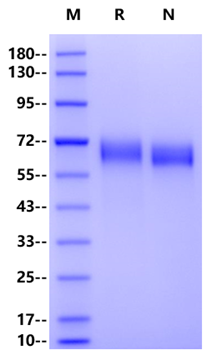
60-70kDa (Reducing)
>95% by SDS-PAGE
· 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
· 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
· 1 week, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
· Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Hyaluronidases are a group of glycosidases catalyzing the degradation of hyaluronic acid (HA). There are six known types (hyaluronidase 1–4, PH-20, and HYALP1). Human hyaluronidase is present both in organs (testis, spleen, skin, eyes, liver, kidneys, uterus, and placenta) and body fluids (tears, blood, and semen). Testicular PH20 hyaluronidase is found on the surface of human sperm and inner acrosomal membrane and degrades hyaluronic acid in the ovum during fertilization. Hyaluronidase PH20 is known as sperm adhesion molecule 1 (SPAM1) and random hydrolysis of (1, 4)-linkages between N-acetyl- beta-D-glucosamine and D-glucuronate residues in hyaluronic acid (HA). PH20/SPAM1 involved in sperm-egg adhesion. Upon fertilization sperm must first penetrate a layer of cumulus cells that surrounds the egg before reaching the zona pellucida. The cumulus cells are embedded in a matrix containing hyaluronic acid which is formed prior to ovulation. PH20/SPAM1 protein aids in penetrating the layer of cumulus cells by digesting hyaluronic acid.