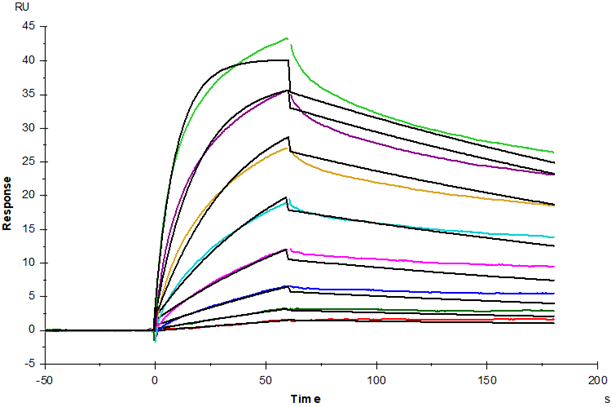
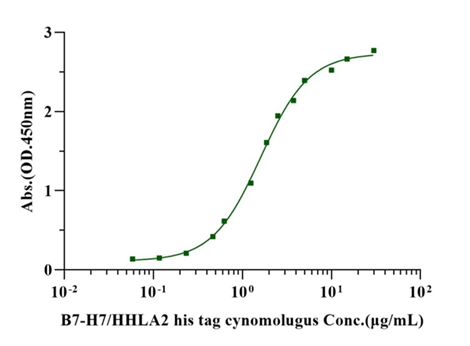
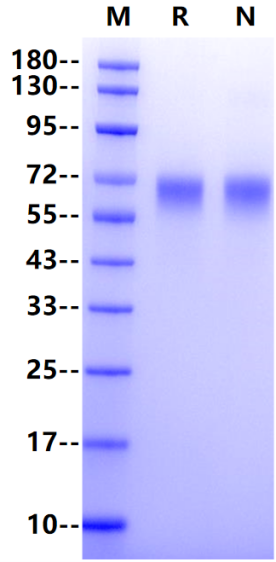
Ile21-Asn345, with C-terminal 8*His IFLSAFFTYVPMNEQIIIGRLGEDIILPSSFERGSEVVIHWKYQDSYNSYNVHSYYKGSGRLESQDTRYANRTSLFYNEIQNGNASLFFRRLSLLDEGIYTCYVGTAIQAITNKVVLKVGVFLTPMMKYEKRNTNSFLICNVLSVYPRPIITWKMDNTPISENNMQETGSLGPFSINSTLNITGSNSSYECTIENSLLKQTWTGRWTMKDGLHKMQSEHVSLSCELVNDYFSPNQDFKVTWSRMESGISSILAYYLSSSQNTTFYESRFSWNKELKNQSDFSMNLTDLSLSDSGEYLCNISSDEYTLLTIHTVHVEPSQETASDNGGGSHHHHHHHH
1、Zhu Y. et al. (2013) B7-H5 costimulates human T cells via CD28H. Nat Commun. 4.
2、Dong Z. et al. (2018) EGFR may participate in immune evasion through regulation of B7-H5 expression in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 18: 3769-3779.
Human endogenous retrovirus-H long terminal repeat-associating protein 2 (HHLA2; also known as B7H7 or B7H5) is the only member of the B7 protein family found in humans. HHLA2 cannot be found in mice and is mainly expressed in human breast, lung, thyroid, melanoma, pancreas, ovary, liver, bladder, colon, prostate, kidney and esophagus cancer cells, activated myeloid cells, monocyte-derived macrophages and dendritic cells. In addition, HHLA2 interacts with the co-receptor CD28H to stimulate T cell proliferation, differentiation and the production of cytokines, including IFN-γ, IL-2 and IL-10. In terms of cancer, higher expression levels of HHLA2 were previously reported to be associated with poorer prognoses or higher degrees of tumour invasion in lung carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma and prostate cancer.