Asp22-Thr414, with C-terminal Mouse IgG2a Fc
DMKGHFDPAKCRYALGMQDRTIPDSDISVSSSWSDSTAARHSRLESSDGDGAWCPAGPVFPKEEEYLQVDLRRLHLVALVGTQGRHAGGLGKEFSRSYRLRYSRDGRRWMDWKDRWGQEVISGNEDPGGVVLKDLGPPMVARLVRFYPRADRVMSVCLRVELYGCLWRDGLLSYTAPVGQTMQLSEVMVHLNDSTYDGYTAGGLQYGGLGQLADGVVGLDDFRQSQELRVWPGYDYVGWSNQSFPTGYVEMEFEFDRLRTFQTMQVHCNNMHTLGARLPGGVECRFKRGPAMAWEGEPVRHALGGSLGDPRARAISVPLGGHVGRFLQCRFLFAGPWLLFSEISFISDVVNDSSDTFPPAPWWPPGPPPTNFSSLELEPRGQQPVAKAEGSPTIEGRMDPEPRGPTIKPCPPCKCPAPNLLGGPSVFIFPPKIKDVLMISLSPIVTCVVVDVSEDDPDVQISWFVNNVEVHTAQTQTHREDYNSTLRVVSALPIQHQDWMSGKEFKCKVNNKDLPAPIERTISKPKGSVRAPQVYVLPPPEEEMTKKQVTLTCMVTDFMPEDIYVEWTNNGKTELNYKNTEPVLDSDGSYFMYSKLRVEKKNWVERNSYSCSVVHEGLHNHHTTKSFSRTPGK
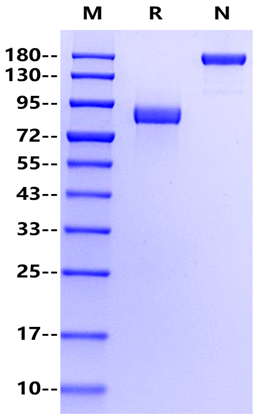
>95% by SDS-PAGE&RP-HPLC
Discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) belongs to a subfamily of tyrosine kinase receptors with an extracellular domain homologous to Dictyostellium discoideum protein discoidin I which are activated by various types of collagens. Receptor tyrosine kinases play a key role in the communication between cells and their microenvironment and they are involved in the regulation of cell growth, differentiation and metabolism. Expression of DDR1 is restricted to epithelial cells, particularly in the kidney, lung, gastrointestinal tract and brain. In addition, DDR1 has been shown to be significantly overexpressed in several human tumors, and it has been demonstrated to be able to promote tumor invasion and metastasis and being closely related to tumor immune infiltration. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene.

Immobilized Cell AdhereTM Type I collagen, Human, Lyophilzed at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind DDR1 mFc Chimera, Mouse (Cat. No. UA010130) with EC50 of 0.48-0.84μg/ml.