Leu33-Arg143, with C-terminal 8*His LWMHKVPASLMVSLGEDAHFQCPHNSSNNANVTWWRVLHGNYTWPPEFLGPGEDPNGTLIIQNVNKSHGGIYVCRVQEGNESYQQSCGTYLRVRQPPPRPFLDMGEGTKNRGGGSHHHHHHHH
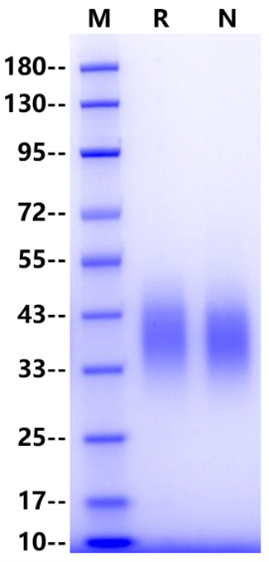
35-46kDa
>95% by SDS-PAGE
Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1、Venkitaraman A R. et al. (1991) The B-cell antigen receptor of the five immunoglobulin classes. Nature. 352(6338): 777-781.
2、Kim K M. et al. (1993) Signalling function of the B-cell antigen receptors. Immunol Rev. 132: 125-146.
CD79A encodes CD79a (also known as Ig-α) belonging to the Ig superfamily, a transmembrane protein that associate with CD79a(Ig-β) via a disulfide bond. CD79A and CD79B encoded by the mb-1 and B29 genes, respectively. CD79A and CD79B are proximal B-cell receptor subunits that contain an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) that frequently harbors somatic mutations. Ig-α and Ig-β form a disulfide-linked heterodimer that associates with membrane-bound Ig (mIg)3 molecules of every Ig class to form the B cell Ag receptor (BCR) complex. The variable region of the H and L (IgH and IgL) chains of the mIg molecules constitute the Ag-binding portion of the BCR, whereas the Ig-α/Ig-β heterodimer is its signaling component.

Immobilized CD79A His Tag Protein, Human (Cat. No. UA010317) at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind CD79a/MB-1 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-030-18) (Cat. No. S0B2200) with EC50 of 1.57-2.04ng/mL.