Asp22-Asn266
DTLESIDNCAVGCPTGGSSNVSIVRHAYTLNNNSTTKFANWVAYHITKDTPASGKTRNWKTDPALNPADTLAPADYTGANAALKVDRGHQAPLASLAGVSDWESLNYLSNITPQKSDLNQGAWARLEDQERKLIDRADISSVYTVTGPLYERDMGKLPGTQKAHTIPSAYWKVIFINNSPAVNHYAAFLFDQNTPKGADFCQFRVTVDEIEKRTGLIIWAGLPDDVQASLKSKPGVLPELMGCKN
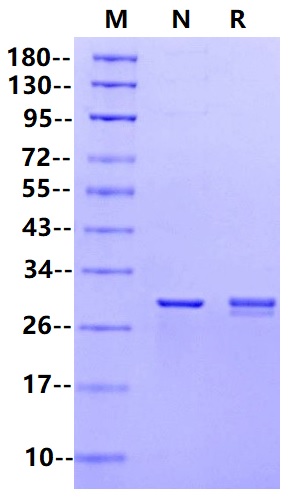
27.7kDa (Reducing)
>95% by SDS-PAGE
10mM Tris (pH7.4), 500mM NaCl, 2mM MgCl2, 50% glycerol
· 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
· 1 week, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
· Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
1.Nestle M, Roberts W K. An Extracellular Nuclease from Serratia marcescens I. PURIFICATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYME[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1969, 244.
2.Kim W Y, Lee H S, Suh S J, et al. Purification and Cellular Localization of Extracellular Nuclease of Serratia marcescens Expressed in Escherichia coli[J]. Korean Journal of Microbiology, 1994, 32(2):147-154.
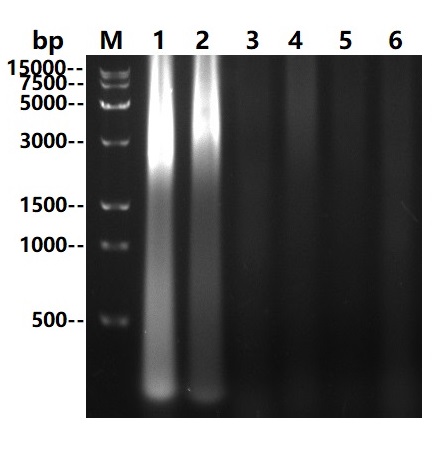
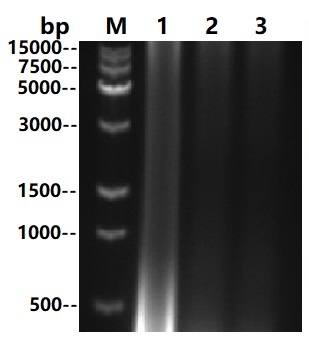
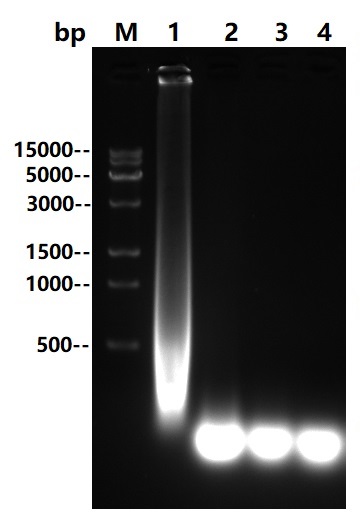
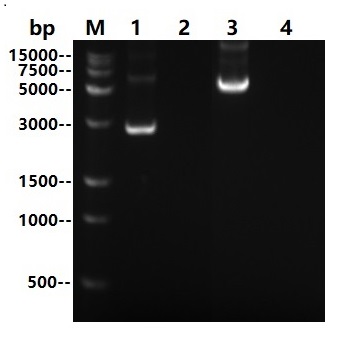
Multi Nuclease all-around nuclease, also called broad-spectrum nucleic acid enzyme, is a kind of comes from Serratia Marcescens restriction endonuclease. It is capable of degradation of all forms of DNA and RNA (double-stranded, single-stranded, linear, circular or superhelical forms) under a very wide range of conditions (6Murea, 0.1M GuanidineHCl, 0.4%TritonX100, 0.1%SDS, 1mM EDTA, 1mM PMSF). The formation of 3-5 oligonucleotide residues containing 5 '-phosphate terminus is widely used to remove nucleic acids from biological products. The expression and purification of this product in Escherichia coli(E.coli) through genetic engineering can not only reduce the viscosity of cell supernatant and cell lysate in scientific research, but also improve the efficiency of protein purification and functional research. It can also be used in virus purification, vaccine production, protein and polysaccharide pharmaceutical industry as a host residual nucleic acid removal reagent, reducing the host residual nucleic acid to the peak (pg) level to improve the efficacy and safety of biological products. And can effectively prevent human peripheral blood monocyte (PBMC) clumping in cell therapy and vaccine research.
|
Components |
Amount |
|
UltraNuclease * |
250U/μL
|
|
Buffer Formulation |
10mM Tris (pH7.4), 500mM NaCl, 2mM MgCl2, 50% glycerol |
* One unit of Nuclease is defined as the amount of enzyme that causes a ∆A260 of 1.0 (equivalent to the complete digestion of 37μg DNA) in 30min.
1.Sample preparation:
Adherent cells: Remove the medium, clean the cells with PBS, and remove the supernatant.
Suspension cells: Cells were collected by centrifugation, cleaned with PBS, centrifuged at 6,000rpm for 10min, and precipitates were collected.
Escherichia coli: The bacteria were collected by centrifugation, cleaned once with PBS, centrifuged at 8,000rpm for 5min, and precipitates were collected.
2.Sample treatment:
The collected cell precipitates are cleaved according to the ratio of mass (g) to volume (mL) to 1: (10~20). Cells can also be cleaved mechanically or chemically on ice or at room temperature (1g cells are about 109).
3.Enzyme addition:
the proportion of 1g cell precipitation digested by 250Units is required. You can also choose the addition plan according to the recommended dosage in the table above, increase the amount of enzyme within a certain range, and reduce the digestion time accordingly.
4.Supernatant acquisition:
The supernatant of cell lysis solution was obtained by centrifugation at 12,000rpm for 30min, and then subsequent related experiments were conducted.
|
Conditional parameter |
Optimum condition |
Applicable condition |
|
Mg2+ |
1-2mM |
1-10mM |
|
PH |
8.0 |
6-10 |
|
Temperature |
37℃ |
0-42℃ |
|
DTT |
0-100mM |
>0mM |
|
β-Me |
0-100mM |
>0mM |
|
Monovalent cation |
0-20mM |
0-150mM |
|
phosphate anion |
0-10mM |
0-100mM |
One unit of Nuclease is defined as the amount of enzyme that causes a ∆A260 of 1.0 (equivalent to the complete digestion of 37μg DNA) in 30min