Lys26-Trp390, with C-terminal 8*His KKVVLGKKGDTVELTCTASQKKSIQFHWKNSNQIKILGNQGSFLTKGPSKLNDRADSRRSLWDQGNFPLIIKNLKIEDSDTYICEVEDQKEEVQLLVFGLTANSDTHLLQGQSLTLTLESPPGSSPSVQCRSPRGKNIQGGKTLSVSQLELQDSGTWTCTVLQNQKKVEFKIDIVVLAFQKASSIVYKKEGEQVEFSFPLAFTVEKLTGSGELWWQAERASSSKSWITFDLKNKEVSVKRVTQDPKLQMGKKLPLHLTLPQALPQYAGSGNLTLALEAKTGKLHQEVNLVVMRATQLQKNLTCEVWGPTSPKLMLSLKLENKEAKVSKREKAVWVLNPEAGMWQCLLSDSGQVLLESNIKVLPTWGGGSHHHHHHHH
45-50kDa
1、Farrar W L. et al. (1988) Characterization of CD4 glycoprotein determinant-HIV envelope protein interactions: perspectives for analog and vaccine development. Crit Rev Immunol. 8(4): 315-339.
2、Biddison W E. et al. (1989) CD4 expression and function in HLA class II-specific T cells. Immunol Rev. 109: 5-15.
3、Singh S K. et al. (2012) Mapping the interaction between the cytoplasmic domains of HIV-1 viral protein U and human CD4 with NMR spectroscopy. FEBS J. 279(19): 3705-3714.
T-cell surface glycoprotein CD4 is also known as T-cell surface antigen T4/Leu-3 that plays an essential role in the immune response and serves multiple functions in responses against both external and internal offenses. In T-cells, functions primarily as a coreceptor for MHC class II molecule: peptide complex. The antigens presented by class II peptides are derived from extracellular proteins while class I peptides are derived from cytosolic proteins. Interacts simultaneously with the T-cell receptor (TCR) and the MHC class II presented by antigen presenting cells (APCs).CD4 is accessory protein for MHC class-II antigen/T-cell receptor interaction. CD4 induces the aggregation of lipid rafts. CD4 is a primary receptor used by HIV-1 to gain entry into host T cells. HIV infection leads to a progressive reduction of the number of T cells possessing CD4 receptors.
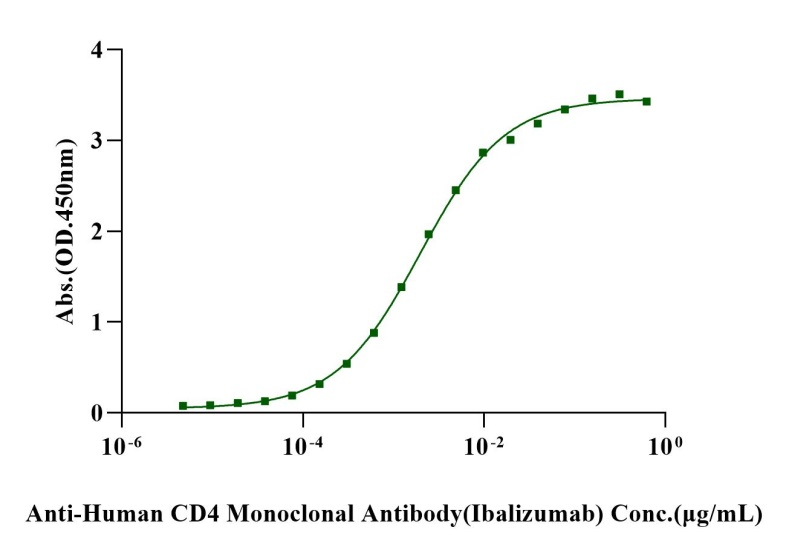
Immobilized CD4/LEU3 His Tag, Human (Cat. No. UA010353) at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind Anti-Human CD4 Monoclonal Antibody (Ibalizumab) with EC50 of 1.80-2.15ng/mL.