Gly17-Ser200, with C-10*His GMRTEDLPKAVVFLEPQWYSVLEKDSVTLKCQGAYSPEDNSTQWFHNESLISSQASSYFIDAATVNDSGEYRCQTNLSTLSDPVQLEVHIGWLLLQAPRWVFKEEDPIHLRCHSWKNTALHKVTYLQNGKDRKYFHHNSDFHIPKATLKDSGSYFCRGLVGSKNVSSETVNITITQGLAVSTISGGGSGGGSHHHHHHHHHH
>95% by SDS-PAGE
IgG Fc receptor (Fc γ R) is a member of the Ig superfamily, which plays a role in activating or inhibiting immune response. Human Fc γ Rs is identified as three types: RI (CD64), RII (CD32) and RIII (CD16). CD16 is a low-affinity Fc receptor, which has been identified as Fc receptor Fc γ RIII (a (CD16a) and Fc γ RIIIb (CD16b). CD16b is a single-chain molecule containing an ITIM motif in the cytoplasmic domain and is specifically expressed by neutrophils and stimulated eosinophils. CD16b can bind IgG in monomeric, complex or aggregated forms. CD16 has three allelic variants NA-1, NA-2 and SH. CD16 inhibits multiple cellular functions such as B cell activation/proliferation and mast cell degranulation, fails to mediate antibody-dependent cytotoxicity and phagocytosis, acts as a trap for peripheral circulating immune complexes, binds IgG complexes but does not activate neutrophils. By interacting with CR3 and CR4, CD16 induces monocytes to produce IL-6 and IL-8, thereby regulating the inflammatory process.
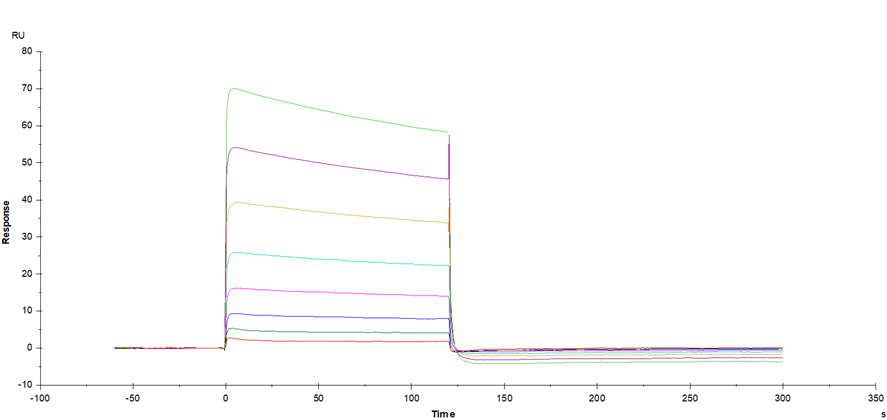
Anti-His antibody Immobilized on CM5 Chip captured CD16b (NA2) His Tag, Human (Cat. No. UA020021), can bind IgG1-Fc (UA050001) with an affinity constant of 6.144 μM as determined in SPR assay (Biacore T200).

Anti-His antibody Immobilized on CM5 Chip captured Fc γ RIIIB/CD16b (NA2) His Tag, Human (Cat. No. UA020021), can bind Rituximab with an affinity constant of 0.83 μM as determined in SPR assay.