Gln35-Gly428, with C-terminal 8*His QLTTESMPFNVAEGKEVLLLVHNLPQQLFGYSWYKGERVDGNRQIVGYAIGTQQATPGPANSGRETIYPNASLLIQNVTQNDTGFYTLQVIKSDLVNEEATGQFHVYPELPKPSISSNNSNPVEDKDAVAFTCEPETQDTTYLWWINNQSLPVSPRLQLSNGNRTLTLLSVTRNDTGPYECEIQNPVSANRSDPVTLNVTYGPDTPTISPSDTYYRPGANLSLSCYAASNPPAQYSWLINGTFQQSTQELFIPNITVNNSGSYTCHANNSVTGCNRTTVKTIIVTELSPVVAKPQIKASKTTVTGDKDSVNLTCSTNDTGISIRWFFKNQSLPSSERMKLSQGNTTLSINPVKREDAGTYWCEVFNPISKNQSDPIMLNVNYNALPQENGLSPGGGGSHHHHHHHH
1、Tsugawa N. et al. (2021) CEACAM1 specifically suppresses B cell receptor signaling-mediated activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 535: 99-105.
Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein and a member of the CEA family. The extracellular domain of CEACAM1 consists of a membrane-distal immunoglobulin (Ig)V-like N-region and variable numbers of alternating IgC1- and IgC2-like proximal regions. Therefore, this molecule is also classified as a member of the Ig supergene family. Several heterophilic ligands for the N-domain of CEACAM1 have been reported. However, homophilic ligation of the N-domains of CEACAM1 with another N-domain of CEACAM1 is the predominant means of physiologic interaction. CEACAM1 has been reported to be involved in several functions such as tumor growth, angiogenesis, endocrine function and immunology in humans and rodents.
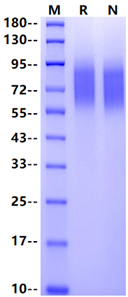
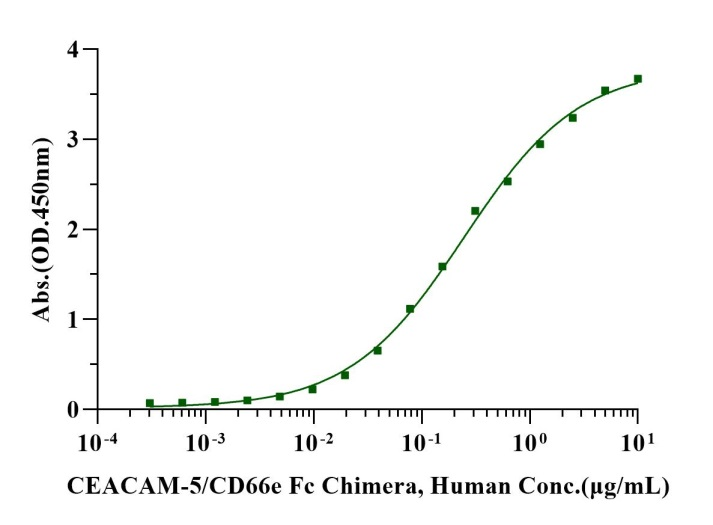
Immobilized CEACAM-1/CD66a His Tag, Human (Cat. No. UA010389) at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind CEACAM-5/CD66e Fc Chimera, Human (Cat. No. UA010368) with EC50 of 0.21-0.29μg/mL .