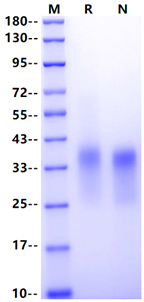
Ala26-Pro180, with C-terminal 8*His
AQEVQQSPHCTIAPVGGSVNITCSTSGELHGIYLRQLGPQPQNIIYYEDRVVPTTDKRFQGRIDFSGSQDNLTITMHHLQPSDTGTYTCQAVTEINVYGSGTLVLVTEEQSQGLHRCSDAPPTGSALPVPPTTSALPALPTASALPALPTASALPGGGSHHHHHHHH
1、Sempowski G D. et al. (1999) Resistance of CD7-deficient mice to lipopolysaccharide-induced shock syndromes. J Exp Med. 189(6): 1011-1016.
CD7 is a 40-kD member of the Ig gene superfamily that is expressed on a major subset of human peripheral T lymphocytes and NK cells. CD7 is an early T cell activation antigen in that CD7 mRNA levels rise within 15 min after initiation of a transmembrane calcium ion flux. CD7 can complex with CD3 and CD45 molecules, and CD7 signaling involves both protein kinase C and protein tyrosine kinase. CD7 has been shown to be a functional signal-transducing molecule on resting NK cells. Antibody cross-linking of NK cell CD7 induced increases in free cytoplasmic calcium, secretion of IFN-γ, NK cell proliferation, adhesion to fibronectin, and NK cytotoxic activity. Although the above studies have demonstrated in vitro roles for CD7 in T and NK cell activation and/or adhesion, relevant functions of CD7 in vivo remain unknown.
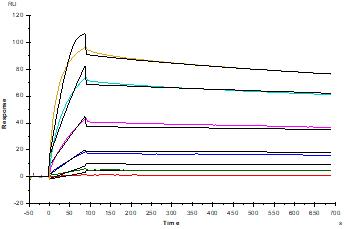
Protein A Chip captured CD7 Ligand/SECTM1 Fc Chimera, Human (Cat. No. UA010409), can bind . CD7 His Tag, Cynomolgus (Cat. No. UA010397) with an affinity constant of 0.35nM as determined in SPR assay .