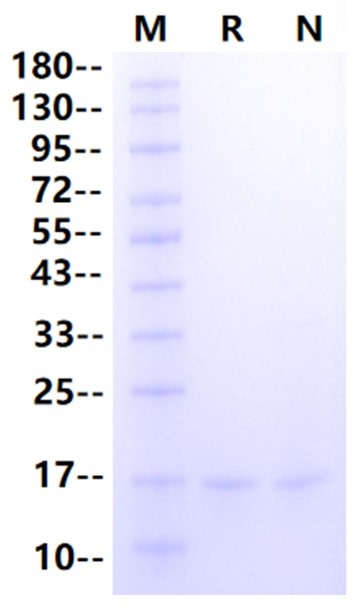
>95%, by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions
Fatty acid-binding protein 3 (FABP3) is a cytosolic protein found in various tissues, including heart, skeletal muscle, intestinal mucosa, liver, and kidney. It is also highly expressed in the adult brain, particularly in the pons, frontal lobe, and hippocampus. In the brain, FABP3 regulates the lipid composition of the membrane and transports fatty acids between different intracellular compartments. It is released extracellularly after neuronal damage and high cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentration of FABP3 is found in acute conditions, such as brain injury and stroke. CSF FABP3 concentration is also higher in conditions with neuro degeneration/neuronal damage, e.g., Alzheimer’s disease (AD), mild cognitive impairment (MCI) due to AD, dementia with Lewy bodies, and Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. CSF FABP3 concentration correlates with cognitive decline and are associated with brain volume loss in areas selectively affected in early AD. Thus, FABP3 is suggested to be a general marker of neuronal damage.