95-120kDa
Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1、Arshad N. et al. (2013) Site-specific N-Linked Glycosylation of Receptor Guanylyl Cyclase C Regulates Ligand Binding, Ligand-mediated Activation and Interaction with Vesicular Integral Membrane Protein 36. J. Biol. Chem. 288(6):3907-3917.
1、Gibbons A V. et al. (2013) Intestinal GUCY2C Prevents TGF-β Secretion Coordinating Desmoplasia and Hyperproliferation in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 73(22): 6654-6666.
Guanylyl Cyclase C (GUCY2C), also known as heat-stable enterotoxin receptor, is a type I transmembrane protein of the guanylate cyclase (GC) family expressed by intestinal epithelial cells from the duodenum to rectum. Mature human GUCY2C consists of an extracellular domain (ECD) with a ligand binding domain, a transmembrane segment and a cytoplasmic region possessing a kinase and GC catalytic domain. Endogenous ligands of GUCY2C include guanylin and uroguanylin. GUCY2C in epithelial cells plays an important role in cell dynamics and homeostatic balance of proliferation, metabolism, and differentiation that organizes the guanylyl cyclase C hormone axis. GUCY2C is also expressed in the brain and is implicated in attention deficiency and hyperactive behavior. The activation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a second intracellular messenger, can stimulate the production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (CGMP), which plays a role in regulating homeostasis, maintaining intestinal barrier function, and exerting anti-inflammatory activity.
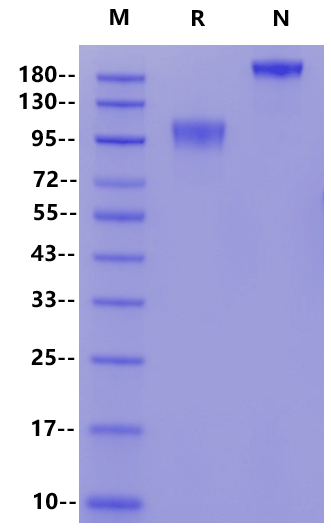
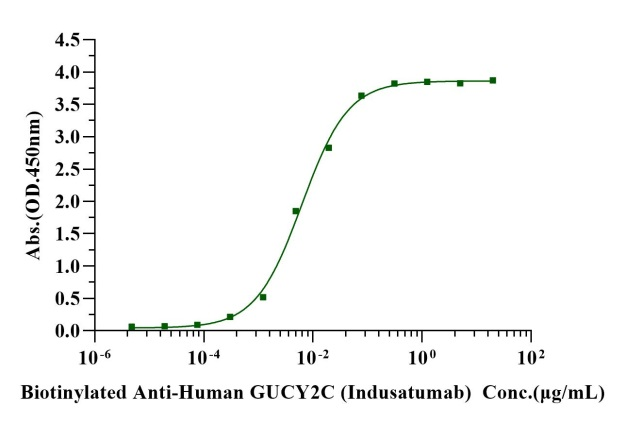
Immobilized GUCY2C Fc Chimera Protein, Human (Cat. No. UA010217) at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind Biotinylated Anti-Human GUCY2C (Indusatumab) with EC50 of 5.26-7.52 ng/ mL.