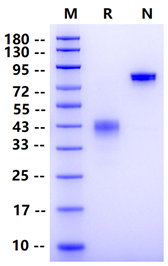
Met1-Ala54, with C-terminal Human IgG1 Fc &Avi tag
MLQMAGQCSQNEYFDSLLHACIPCQLRCSSNTPPLTCQRYCNASVTNSVKGTNAIEGRMDPKSSDKTHTCPPCPAPELLGGPSVFLFPPKPKDTLMISRTPEVTCVVVDVSHEDPEVKFNWYVDGVEVHNAKTKPREEQYNSTYRVVSVLTVLHQDWLNGKEYKCKVSNKALPAPIEKTISKAKGQPREPQVYTLPPSRDELTKNQVSLTCLVKGFYPSDIAVEWESNGQPENNYKTTPPVLDSDGSFFLYSKLTVDKSRWQQGNVFSCSVMHEALHNHYTQKSLSLSPGKGLNDIFEAQKIEWHE
38-45kDa (Reducing)
1.Nina Shah, Ajai Chari, Emma Scott, Khalid Mezzi& Saad Z. Usmani: B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in multiple myeloma:rationale for targeting and current therapeutic approaches, Leukemia volume 34, pages985–1005 (2020).
BCMA (The B-cell maturation antigen), also designated as TNFRSF17, belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, which is a family of cytokine receptors. BCMA is encoded by a 2.92-kb TNFRSF17 gene located on the short arm of chromosome 16 (16p13.13) and composed of 3 exons separated by 2 introns. There are four natural splice variants of human BCMA that present with different receptor binding affinities, membrane-anchoring ability, and intracellular domain signaling. BCMA main ligands are the cytokines B-cell activating factor and a proliferation-inducing ligand. The interaction between BCMA and its ligands activates the NF-κB signaling pathway that plays an important role in B-cell proliferation and maturation and is essential for the survival of long-lived bone marrow plasma cells. BCMA is expressed preferentially on mature B cells and has minimal expression on hematopoietic stem cells or other cell types. The BCMA has emerged as a central target in multiple myeloma (MM). In preclinical studies, overexpression of BCMA and the interaction with is ligand, a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL), was found to promote MM progression in vivo and augment MM cell growth and survival through induction of multiple signaling cascades, including protein kinase B (AKT), MAPK, and nuclear factor (NF)-κB. Additionally, BCMA has been shown to be solubilized at high levels in serum of patients with MM (sBCMA). This form of sBCMA binds to B-cell activating factor (BAFF). The role of BAFF is to stimulate normal B-cell and plasma cell development; however, this functioning is prevented when it is bound by BCMA in the serum, thereby leading to decreased polyclonal immunoglobulin levels in patients with MM.
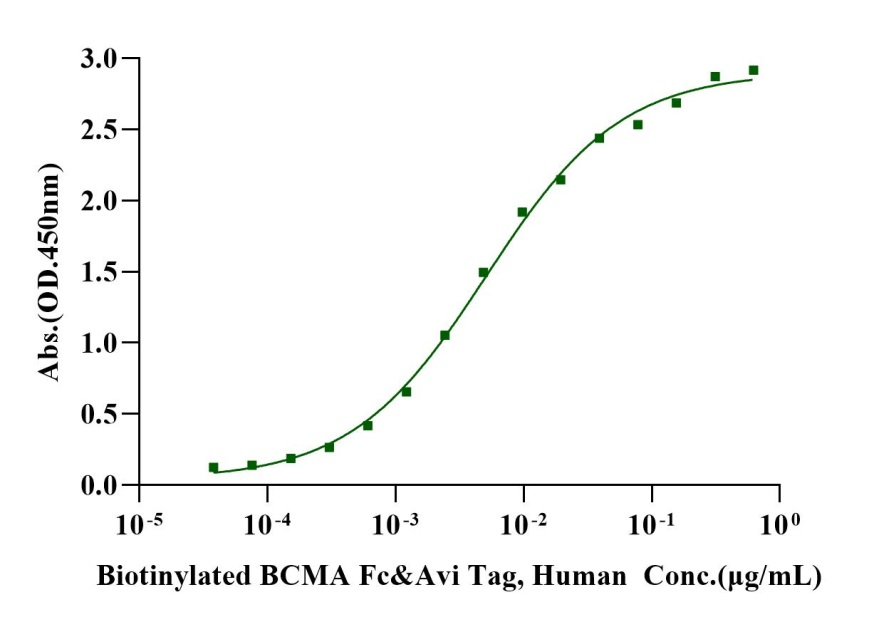
Immobilized Anti-Human BCMA Monoclonal Antibody (Belantamab) at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind Biotinylated BCMA Fc&Avi Tag, Human (Cat. No. UA010461)with EC50 of 4.30-6.13ng/mL.