Lys24-Trp454, with C-terminal Mouse mIgG2a Fc
KHPDDFRVVGPNLPILAKVGEDALLTCQLLPKRTTAHMEVRWYRSDPDMPVIMYRDGAEVTGLPMEGYGGRAEWMEDSTEEGSVALKIRQVQPSDDGQYWCRFQEGDYWRETSVLLQVAALGSSPNIHVEGLGEGEVQLVCTSRGWFPEPEVHWEGIWGEKLMSFSENHVPGEDGLFYVEDTLMVRNDSVETISCFIYSHGLRETQEATIALSERLQTELASVSVIGHSQPSPVQVGENIELTCHLSPQTDAQNLEVRWLRSRYYPAVHVYANGTHVAGEQMVEYKGRTSLVTDAIHEGKLTLQIHNARTSDEGQYRCLFGKDGVYQEARVDVQVMAVGSTPRITREVLKDGGMQLRCTSDGWFPRPHVQWRDRDGKTMPSFSEAFQQGSQELFQVETLLLVTNGSMVNVTCSISLPLGQEKTARFPLSGWIEGRMDPEPRGPTIKPCPPCKCPAPNLLGGPSVFIFPPKIKDVLMISLSPIVTCVVVDVSEDDPDVQISWFVNNVEVHTAQTQTHREDYNSTLRVVSALPIQHQDWMSGKEFKCKVNNKDLPAPIERTISKPKGSVRAPQVYVLPPPEEEMTKKQVTLTCMVTDFMPEDIYVEWTNNGKTELNYKNTEPVLDSDGSYFMYSKLRVEKKNWVERNSYSCSVVHEGLHNHHTTKSFSRTPGK
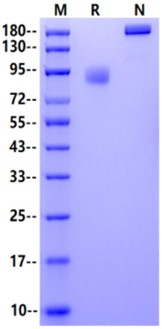
72-95kDa (Reducing)
1.Arnett, H.A. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 178:1523.
2.Arnett, H.A. et al. (2009) Cytokine 46:370.
3.Smith, I.A. et al. (2010) J. Immunol. 184:3514.
4.Nguyen, T. et al. (2006) J. Immunol. 176:7354.
Butyrophilin-like 2 (BTNL2) is a member of the BTN/MOG Ig-superfamily and functions as a negative regulator of immune cell activation.BTNL2 is expressed in epithelial cells of the small intestine, colonic dendritic cells, and in cells of the lymph node. BTNL2 expression is upregulated in T cells following activation, a characteristic BTNL2 shares with the homologous B7 family of co-stimulatory molecules. BTNL2 negatively regulates T cells by inhibiting proliferation and inflammatory cytokine secretion. It also increases the expression of FoxP3 in T cells to promote regulatory T cell development. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in BTNL2 are associated with a risk for sporadic prostate cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, sarcoidosis, ulcerative colitis, and other inflammatory diseases.