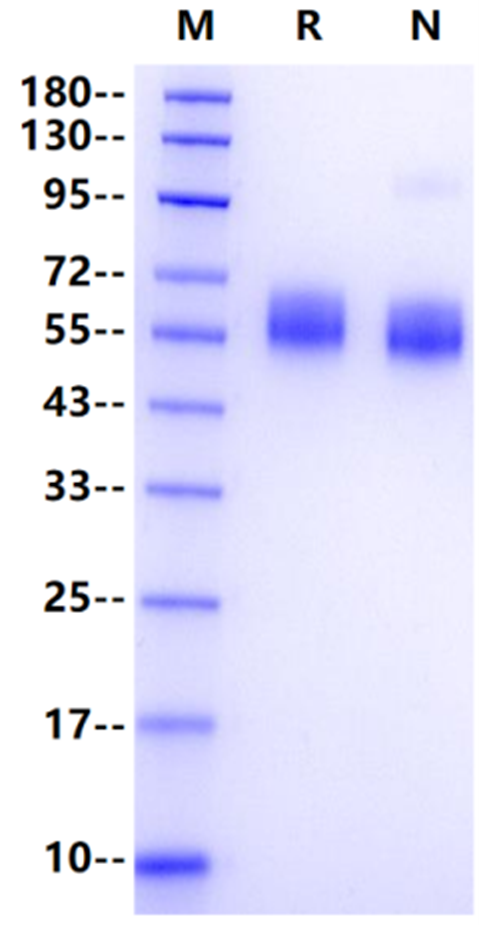
Lys19-Phe328, with C-terminal 8* His
KFSKQSWGLENEALIVRCPRQGKPSYTVDWYYSQTNKSIPTQERNRVFASGQLLKFLPAAVADSGIYTCIVRSPTFNRTGYANVTIYKKQSDCNVPDYLMYSTVSGSEKNSKIYCPTIDLYNWTAPLEWFKNCQALQGSRYRAHKSFLVIDNVMTEDAGDYTCKFIHNENGANYSVTATRSFTVKDEQGFSLFPVIGAPAQNEIKEVEIGKNANLTCSACFGKGTQFLAAVLWQLNGTKITDFGEPRIQQEEGQNQSFSNGLACLDMVLRIADVKEEDLLLQYDCLALNLHGLRRHTVRLSRKNPSKECFGGGSHHHHHHHH
1.Savenije O E. et al. (2011) Interleukin-1 receptor-like1 polymorphisms are associated with serum IL1RL1-a, eosinophils, and asthma inchildhood. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 127(3): 750-756.
2.Li H. et al. (2000) The cloning and nucleotidesequence of human ST2L cDNA. Genomics. 67(3): 284-290.
ST2, also known as IL-1 R4 and T1, is an Interleukin-1 receptor family glycoprotein that contributes to Th2 immune responses. Human ST2 consists of a 310 amino acid extracellular domain (ECD) with three Ig-like domains, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 207 aa cytoplasmic domain with an intracellular TIR domain. ST2 is expressed on the surface of mast cells, activated Th2 cells, macrophages, and cardiac myocytes. It binds IL-33, a cytokine that is upregulated by inflammation or mechanical strain in smooth muscle cells, airway epithelia, keratinocytes, and cardiac fibroblasts. IL-33 binding induces the association of ST2 with IL-1R AcP, a shared signaling subunit that also associates with IL-1 RI and IL-1 R rp2. In macrophages, ST2 interferes with signaling from IL-1 RI and TLR4 by sequestering the adaptor proteins MyD88 and Mal. In addition to its role in promoting mast cell and Th2 dependent inflammation, ST2 activation enhances antigen induced hypernociception and protects from atherosclerosis and cardiac hypertrophy. Upon tissue injury, induces UCP2-dependent mitochondrial rewiring that attenuates the generation of reactive oxygen species and preserves the integrity of Krebs cycle required for persistent production of itaconate and subsequent GATA3-dependent differentiation of inflammation-resolving alternatively activated macrophages.