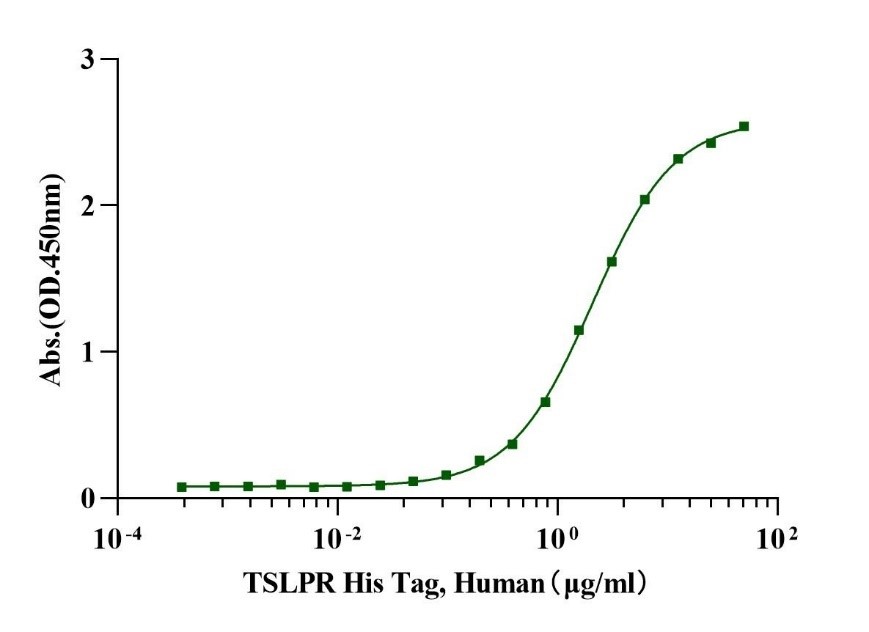
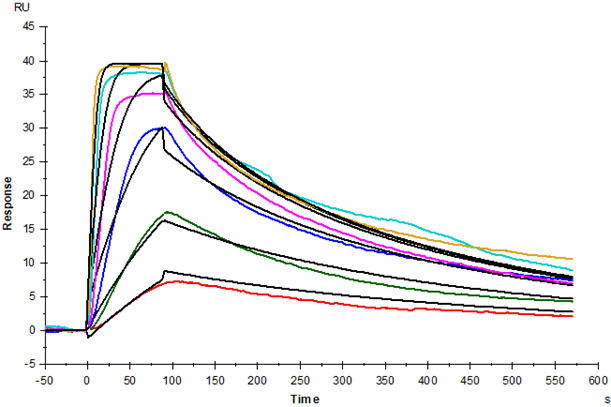
Gln23-Lys231, with C-terminal 8* His
QGGAAEGVQIQIIYFNLETVQVTWNASKYSRTNLTFHYRFNGDEAYDQCTNYLLQEGHTSGCLLDAEQRDDILYFSIRNGTHPVFTASRWMVYYLKPSSPKHVRFSWHQDAVTVTCSDLSYGDLLYEVQYRSPFDTEWQSKQENTCNVTIEGLDAEKCYSFWVRVKAMEDVYGPDTYPSDWSEVTCWQRGEIRDACAETPTPPKPKLSKGGGSHHHHHHHH
1.L S Park. Cloning of the murine thymic stromallymphopoietin (TSLP) receptor: Formation of a functional heteromeric complexrequires interleukin 7 receptor. J Exp Med. 2000 Sep 4;192(5):659-70.
The TSLP receptor (TSLPR, CRLM-2), a typical heterodimeric cytokine receptor consisting of a TSLP binding subunit (TSLPRα) and the α-subunit of the IL-7 receptor (IL-7Rα). TSLPR mRNA has been detected on many immune cell types, including dendritic cells (DCs), T cells, B cells, mast cells, NKT cells and monocytes as well as in tissues from heart, skeletal muscle, kidney and liver. TSLPR has low affinity for TSLP, but in combination with IL-7Rα generates a high affinity binding site for TSLP and triggers signaling. The TSLPR regulates target gene expression via the JAK/STAT signalling pathway with participation of signal transducers and activators of transcription STAT3, STAT5 and STAT1. Genetic, experimental, and clinical evidence suggests that the TSLP-TSLPR pathway is associated with the pathogenesis of allergic diseases such as atopic dermatitis (AD) and asthma.