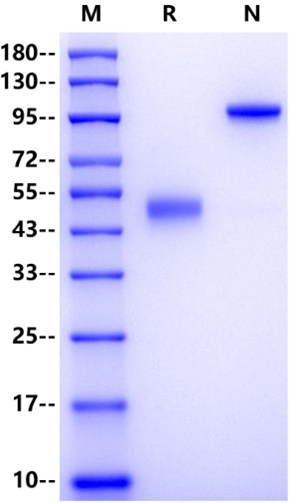
Gln24-Arg152, with C-terminal Human IgG1 Fc QNLDSMLHGTGMKSDSDQKKSENGVTLAPEDTLPFLKCYCSGHCPDDAINNTCITNGHCFAIIEEDDQGETTLASGCMKYEGSDFQCKDSPKAQLRRTIECCRTNLCNQYLQPTLPPVVIGPFFDGSIRIEGRMDPKSSDKTHTCPPCPAPELLGGPSVFLFPPKPKDTLMISRTPEVTCVVVDVSHEDPEVKFNWYVDGVEVHNAKTKPREEQYNSTYRVVSVLTVLHQDWLNGKEYKCKVSNKALPAPIEKTISKAKGQPREPQVYTLPPSRDELTKNQVSLTCLVKGFYPSDIAVEWESNGQPENNYKTTPPVLDSDGSFFLYSKLTVDKSRWQQGNVFSCSVMHEALHNHYTQKSLSLSPGK
1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Mar 5;99(5):2878-83. Epub 2002 Feb 19.
2. Gorczynski, R.M. (2005) Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs 6:483. 3. Barclay, A.N. et al. (2002) Trends Immunol. 23:285.
Activin receptor-Like Kinase 3 (ALK-3), also known as Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptor, type IA (BMPR1A), is a type I receptor for bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) which belong to the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) superfamily. The bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptors are a family of transmembrane serine/threonine kinases that include the type I receptors BMPR1A (this protein) and BMPR1B and the type II receptor BMPR2. ALK-3 plays an essential role in the formation of embryonic ventral abdominal wall, and abrogation of BMP signaling activity due to gene mutations in its signaling components could be one of the underlying causes of omphalocele at birth.