Phe19-Arg238, with C-terminal Avi&His Tag FTVTVPKDLYVVEYGSNMTIECKFPVEKQLDLAALIVYWEMEDKNIIQFVHGEEDLKVQHSSYRQRARLLKDQLSLGNAALQITDVKLQDAGVYRCMISYGGADYKRITVKVNAPYNKINQRILVVDPVTSEHELTCQAEGYPKAEVIWTSSDHQVLSGKTTTTNSKREEKLFNVTSTLRINTTTNEIFYCTFRRLDPEENHTAELVIPELPLAHPPNERGGGSGLNDIFEAQKIEWHEHHHHHHHH
1. Joel Sunshine, Janis M Taube: PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, Current Opinion in Pharmacology, Volume 23, August 2015, Pages 32-38.
PDL1 is a cell surface immunoglobulin superfamily with two Ig-like domains within the extracellular region and a short cytoplasmic domain. PDL1 is also known as B7-H, B7H1, MGC142294, MGC142296, PD-L1, PDCD1L1 and PDCD1LG1,which is a member of the growing B7 family of immune molecules and is involved in the regulation of cellular and humoral immune responses. PD-L1 provides a molecular stop signal to the adaptive immune system helping to distinguish between self and foreign antigens. PDL1 may inhibit ongoing T-cell responses by inducing apoptosis and arresting cell-cycle progression. Many cancers exhibit upregulated PD-L1 protein expression, and several cancers with high levels of PD-L1 have been associated with increased tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis. Using new therapeutics that block the PD-L1:PD-1 interaction has proven successful in the clinic for many cancer types and has sparked great interest in the field of cancer immunotherapy.
1μg (R: reducing conditions, N: non-reducing conditions).
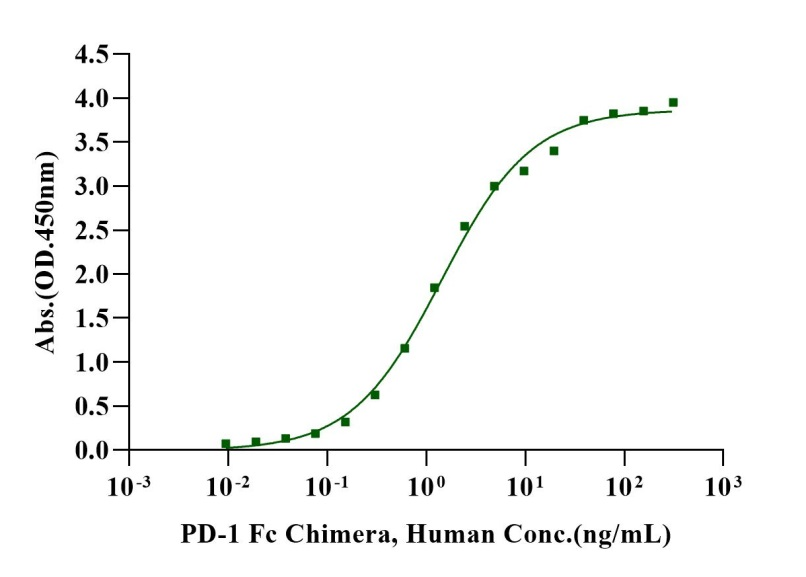
Immobilized Biotinylated PD-L1 Avi&His Tag, Human (Cat. No. UA010541) at 2 μg/mL on Streptavidin precoated (0.5μg/well) plate, can bind PD-1 Fc Chimera, Human (Cat. No. UA010002) with EC50 of 1.21-1.70 ng/ml.