Asn252-Thr356, with N-terminal 6*His
MHHHHHHNSTNLPRNPSMADYEARIFTFGTWIYSVNKEQLARAGFYALGEGDKVKCFHCGGGLTDWKPSEDPWEQHAKWYPGCKYLLEQKGQEYINNIHLTHSLEECLVRTT
1、Holcik M. et al. (2000) Functional Characterization of the X-Linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis (XIAP) Internal Ribosome Entry Site Element: Role of La Autoantigen in XIAP Translation. Mol Cell Biol. 20(13): 4648-57.
2、Winsauer G. et al. (2008) XIAP regulates bi-phasic NF-kappaB induction involving physical interaction and ubiquitination of MEKK2. Cell Signal. 20(11): 2107-12.
3、Suzuki Y. et al. (2001) X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) inhibits caspase-3 and -7 in distinct modes. J Biol Chem. 276(29): 27058-63.
XIAP is a direct inhibitor of caspase-3 and -7, and suppresses the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway by inhibiting caspase-9. XIAPs comprised of 6 exons that encode XIAP, a 497 amino-acid protein whose functions include regulation of apoptosis and promotion of intracellular signaling during innate immunity. Currently, approximately 25 distinct XIAP mutations have been reported in patients with XIAP deficiency. Mutations reduce XIAP expression in half to two-thirds of patients, but missense mutations and C-terminal nonsense mutations or deletions allow for varying levels of expression of mutant protein. As is the case with SAP deficiency, female XIAP mutation carriers are asymptomatic. However, unlike SH2D1A carriers, XIAP carriers typically demonstrate skewed lyonization in lymphocytes in favor of cells retaining wild-type XIAP expression.
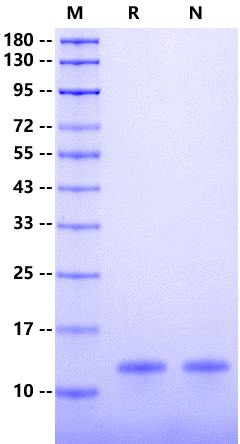
3μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).