Glu22-Cys213, with C-terminal Human IgG1 Fc &Avi tag ELCDDDPPEIPHATFKAMAYKEGTMLNCECKRGFRRIKSGSLYMLCTGNSSHSSWDNQCQCTSSATRNTTKQVTPQPEEQKERKTTEMQSPMQPVDQASLPGHCREPPPWENEATERIYHFVVGQMVYYQCVQGYRALHRGPAESVCKMTHGKTRWTQPQLICTGEMETSQFPGEEKPQASPEGRPESETSCIEGRMDPKSSDKTHTCPPCPAPELLGGPSVFLFPPKPKDTLMISRTPEVTCVVVDVSHEDPEVKFNWYVDGVEVHNAKTKPREEQYNSTYRVVSVLTVLHQDWLNGKEYKCKVSNKALPAPIEKTISKAKGQPREPQVYTLPPSRDELTKNQVSLTCLVKGFYPSDIAVEWESNGQPENNYKTTPPVLDSDGSFFLYSKLTVDKSRWQQGNVFSCSVMHEALHNHYTQKSLSLSPGKGLNDIFEAQKIEWHE
1. Nelson B H, Willerford D M. Biology of the interleukin-2 receptor. Adv Immunol. 1998;70:1-81. 2. Schorle H, Holtschke T, Hunig T, Schimpl A, Horak I. Development and function of T cells in mice rendered interleukin-2 deficient by gene targeting. Nature. 1991;352:621-624. 3. Willerford D M, Chen J, Ferry J A, Davidson L, Ma A, Alt F W. Interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain regulates the size and content of the peripheral lymphoid compartment. Immunity. 1995;3:521-530.
Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha (IL2RA) is also known as IL-2R subunit alpha, IL-2-RA, IL2-RA, TAC antigen, p55, CD antigen CD25, is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein. The interaction of interleukin-2 (IL-2) with its receptor (IL-2R) critically regulates the T-cell immune response, and the α chain CD25/IL-2Rα is required for the formation of the high-affinity receptor. Among them, IL-2 plays a major role in the regulation of the magnitude and duration of T-cell activation in the immune responses. IL-2 promotes T-cell proliferation by interacting with its high-affinity receptor composed of three transmembrane polypeptides, the α, β, and γc chains. The α chain (CD25) is induced during T-cell activation, and its association with β and γc chains constitutes the high-affinity receptor. Most of the biologic effects of IL-2 are mediated through the high-affinity complex as evidenced by the almost identical phenotype of mice with targeted inactivation of the genes for IL-2 and IL-2Rα.
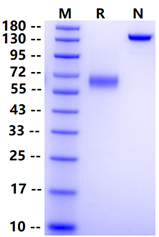
1μg (R: reducing conditions, N: non-reducing conditions).