30-43kDa (Reducing)
Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1.Steinberg MW, et al. (2008) A crucial role for HVEM and BTLA in preventing intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med. 205(6): 1463-76.
2.Pasero C, et al. (2009) A role for HVEM, but not lymphotoxin-beta receptor, in LIGHT-induced tumor cell death and chemokine production. Eur J Immunol. 39(9): 2502-14.
Herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM) is also known as TNFRSF14, TR2 (TNF receptorlike molecule) and ATAR (another TRAF associated receptor), is a type I membrane protein belonging to the TNF/NGF receptor superfamily.It is expressed on many immune cells, including T and B cells, NK cells, monocytes, and neutrophils. Two TNF superfamily ligands lymphotoxin α (TNF-β) and LIGHT (TNFSF14) are identified as cellular ligands for HVEM and initiate the positive signaling. However, recent studies have revealed that HVEM may be viewed as a molecular switch, capable of facilitating both stimulatory and inhibitory cosignaling in T cells. Substantial evidence from both human disease and from experimental mouse models has indicated that dysregulation of the LIGHT-HVEM-BTLA cosignaling pathway can cause inflammation in the lung and in mucosal tissues.
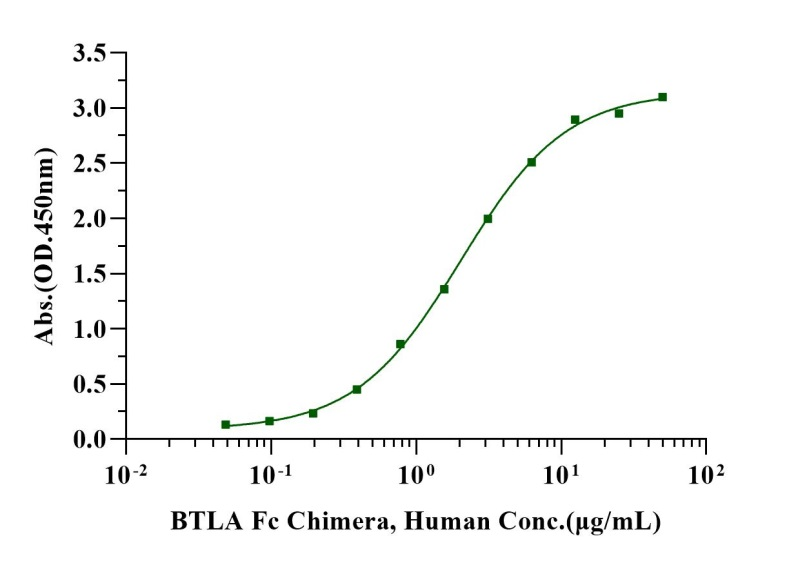
Immobilized HVEM/TNFRSF14, Human (Cat. No. UA010658) at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind BTLA Fc Chimera, Human
(Cat. No. UA010754) with EC50 of 1.86-2.21 μg/mL.
1μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).