90-100kDa (Reducing)
Reconstitute at 0.1-1mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1.Chapoval, A.I. et al. (2001) Nat. Immunol. 2:269. 2.Sharpe, A.H. and G.J. Freeman (2002) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2:116. 3.Coyle, A. and J. Gutierrez-Ramos (2001) Nat. Immunol. 2:203.
Human B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3), also known as CD276, is a member of the B7 family of immune checkpoint molecules, responsible for regulating immune responses.B7 family proteins are type I transmembrane immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily members that contain extracellular Ig V-like and Ig C-like domains with a short cytoplasmic tail. Termed 4IgB7-H3 or B7-H3b, this molecule has two additional Ig-like domains (one V-type and one C-type) and shows a ubiquituous expression pattern. Human B7-H3 is not expressed on resting B cells, T cells, monocytes or dendritic cells, but is induced on dendritic cells and monocytes by inflammatory cytokines. B7-H3 is also overexpressed in numerous cancers including bladder, breast and melanoma.Unlike other B7 family members, human B7-H3 does not bind any known members of the CD28 family of immunoreceptors and its receptor has yet to be identified.B7-H3 has been found to enhance the induction of primary cytotoxic T lymphocytes and stimulate IFN-gamma production.
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).
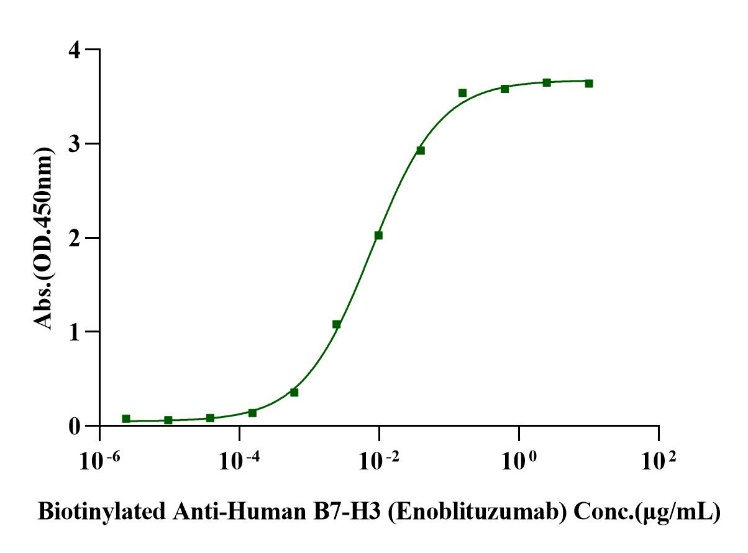
Immobilized B7-H3 (4 Ig)/B7-H3b Fc Chimera Protein, Human (Cat. No. UA010639) at 0.5μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind Biotinylated Anti-Human B7-H3 (Enoblituzumab) with EC50 of 6.72-8.81ng/mL.