1.Yi Jin 1, Angela F Messmer-Blust(2011)Trends Cardiovasc Med.21:1
The transcriptional enhancer factor (TEF)
multigene family is primarily functional in muscle-specific genes through
binding to MCAT elements that activate or repress transcription of many genes
in response to physiological and pathological stimuli. Among the TEF family,
TEF-1, RTEF-1, and DTEF-1 are critical regulators of cardiac and smooth
muscle-specific genes during cardiovascular development and cardiac disorders
including cardiac hypertrophy. Emerging evidence suggests that in addition to
functioning as muscle-specific transcription factors, members of the TEF family
may be key mediators of gene expression induced by hypoxia in endothelial cells
by virtue of its multidomain organization, potential for post-translational
modifications, and interactions with numerous transcription factors, which represent
a cell-selective control mediator of nuclear signaling.
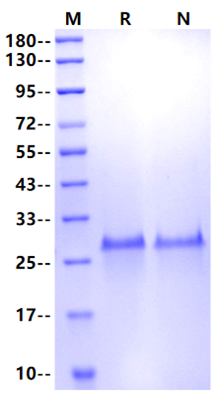
2μg
(R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).