8.7 kDa (Reducing)
>95% by SDS-PAGE
Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010 Feb;21(1):41-8. Epub 2009 Dec 14.
MCP-1, also known as CCL2, is a chemokine belonging to the C-C chemokine family. It plays a crucial role in various physiological processes such as inflammation, immune regulation, and cell migration. MCP-1/CCL2 primarily functions by binding to the C-C chemokine receptor CCR2, thereby guiding monocytes and other inflammatory cells to migrate to sites of inflammation, contributing to the inflammatory response and immune regulation.
Overexpression of MCP-1/CCL2 is closely associated with the pathogenesis and progression of various diseases, including inflammatory diseases, autoimmune disorders, cancer, and metabolic disorders. As a result, MCP-1/CCL2 has emerged as a potential therapeutic target, and researchers are exploring therapeutic strategies targeting MCP-1/CCL2 in the hope of impacting the treatment of related diseases.
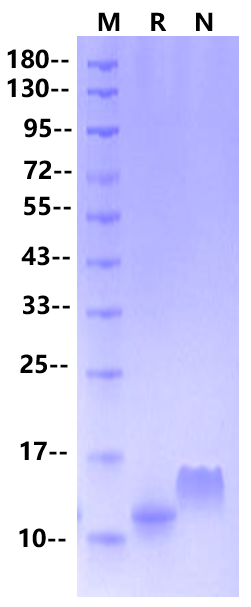
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).